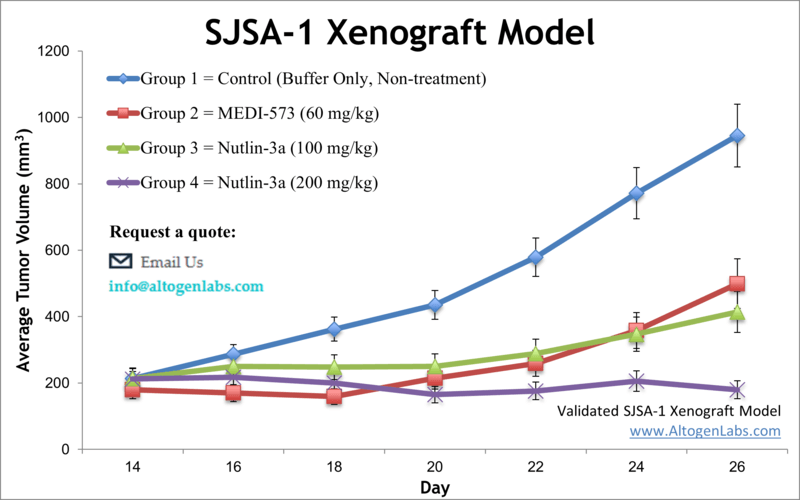
SJSA-1 xenograft model
SJSa-1 is a human synovial sarcoma cell line that is commonly used in research to study synovial sarcoma, a rare type of cancer that affects soft tissues such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles. SJSa-1 cells were originally derived from a biopsy sample from a patient with synovial sarcoma. Sarcoma is a cancer of bones and connective tissues that comprises approximately 20 percent of all childhood cancers, as indicated by the Sarcoma Foundation of America. Cell line derived xenografts (CDX) are based on direct implantation of cancer cell lines into different organs of nude mice and are valuable preclinical models for sarcoma research. The SJSA-1 cell line was isolated in 1982 from the primary tumor of a patient with sarcoma. The SJSA1 cell line overexpresses MDM2 as a mechanism to restrict p53 function. Thus, inhibitors of p53-MDM2 binding that can reactivate p53 in cancer cells could be a useful treatment regimen for sarcoma patients. RG7112 is a potent MDM2 antagonist that binds MDM2, blocking its interactions with p53 in vitro. A 2013 study by Tovar et al. published in Cancer Research investigated antitumor activity of RG7112, using the SJSA-1 xenograft model. Results indicated that RG7112 causes tumor inhibition and regression and is effective in the treatment of tumors expressing wild-type p53. In 2015, Canon et al. released a study using the SJSA-1 model to evaluate the antitumor and p53 effects of AMG 232, an MDM2 inhibitor. Results showed that AMG 232 treatment resulted in a significant increase in p53 activity, cell cycle arrest, a decrease in proliferation, and inhibition of in vivo tumor growth. The group also evaluated combination therapy effects with DNA damaging agents which enhanced tumor regression and p53 signaling, overall supporting the use of AMG232 alone and in combination therapy. Tovar et al. published a Cancer Research article (2013) evaluating RG7112, another selective and potent MDM2 inhibitor, using an array of cancer cell lines including SJSA-1. A crystal structure revealed that RG7112 binds at the p53 pocket of MDM2 and had an overall anticancer effect on the cell lines with varying results in regards to apoptotic activity. In xenografts, tumor inhibition and regression was dose dependent, supporting the use of RG7112 against cancers that express wild type p53. Lastly, Hoffman-Luca et al. released a PLoS One article (2015) which used the SJSA-1 model to study the acquired resistance of another MDM2 inhibitor, SAR405838. Data indicated treatment leads to inhibition of cell growth, increased apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest; results showed prolonged treatment led to varied levels of acquired resistance that may be related to p53 mutations in sublines and subcultures. The SJSA-1 cell line (human bone osteosarcoma) is used to create the CDX SJSA-1 xenograft mouse model. Two main benefits of the SJSA-1 xenograft model is 1) the overexpression of MDM2 that enables the study of small molecule MDM2 antagonists (e.g. nutlin-3), and 2) combination studies that significantly inhibit tumor growth such as ganitumab in combination with mTORC1 inhibitors for the treatment of sarcomas.
SJSA1 Sarcoma Subcutaneous and Metastatic Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs SJSA-1 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- Flasks containing cells are maintained at a phase of exponential population growth.
- The SJSA-1 cells are collected for injection. Cell count and cell viability is determined by trypan blue. The concentration of the cell suspensions are adjusted to the required density and consists of Matrigel + SJSA-1 cells.
- One million cells (1 x 106 cells in 140-200 µL volume) of the cell suspension is injected into the hind leg of each mouse subcutaneously. NOD/SCID or athymic BALB/C mice are used that are 10-12 weeks old.
- Inoculation sites are observed for tumor establishment and digital calipers measure tumors until they reach 200-250 mm3.
- Daily measurements of the tumor and mouse whole-body weights are recorded (2-3 times weekly).
- Tumor tissues are removed and weighed. Remaining tissues are collected and can be frozen (LN2), stabilized (RNA-later reagent), or submersed in 10% NBF formalin.
Get Instant Quote for
SJSA-1 Xenograft Model
Treatment Responses in Metastatic SJSA-1 Osteosarcoma Models
Metastatic SJSA-1 models are widely used in cancer research to study the progression and therapeutic response of osteosarcoma, a rare but aggressive bone cancer. SJSA-1 cells, derived from a human osteosarcoma, are particularly valuable for modeling metastatic disease due to their ability to disseminate to secondary sites such as the lungs and bones. These models help researchers investigate the molecular mechanisms underlying metastasis, including cell migration, invasion, and survival in distant organs. Additionally, metastatic SJSA-1 models provide a platform for testing novel therapies aimed at preventing or treating metastasis. By using in vivo models, researchers can assess the efficacy of targeted treatments, chemotherapies, and immunotherapies in a dynamic tumor microenvironment. Such models are crucial for understanding the challenges in metastasis, which remains a major cause of death in osteosarcoma patients. Overall, metastatic SJSA-1 models are essential for advancing the development of more effective and personalized cancer treatments.
Case Study: Targeting SJSA-1 to Overcome Osteosarcoma Chemoresistance
A study by Pu Y, et al., published by Cell Death and Disease journal, investigates the role of SJSA-1, a chemo-resistant osteosarcoma cell line, in drug resistance mechanisms. SJSA-1 was found to have significantly lower expression of the long noncoding RNA (lncRNA) LAMTOR5-AS1 compared to the chemo-sensitive G-292 cell line. Overexpression of LAMTOR5-AS1 in SJSA-1 reduced its drug resistance, while its knockdown in G-292 increased resistance to chemotherapeutic agents like cisplatin (DDP). The study also identified nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (NRF2) as a key player in SJSA-1-mediated drug resistance. NRF2, known for its role in oxidative stress regulation, was highly expressed in SJSA-1 cells, correlating with increased chemoresistance. Mechanistically, LAMTOR5-AS1 was shown to regulate NRF2 by inhibiting its degradation while impairing its transcriptional activity. Furthermore, NRF2 controlled its own regulation by promoting LAMTOR5-AS1 expression, forming a feedback loop that is disrupted in drug-resistant cells. In vivo experiments using SJSA-1-derived xenografts confirmed that LAMTOR5-AS1 overexpression enhanced chemosensitivity, suggesting a potential therapeutic strategy. These findings highlight the critical role of SJSA-1 in osteosarcoma chemoresistance and suggest that targeting LAMTOR5-AS1 and NRF2 may help improve treatment outcomes.
Additional Case Study: Targeting Endosialin in SJSA-1 Osteosarcoma Models
In a study conducted by Capone E, et al., published by Oncotarget journal, researchers explored the efficacy of a novel antibody-drug conjugate (ENDOS/ADC) targeting endosialin, a surface receptor highly expressed in sarcomas, using SJSA-1 osteosarcoma xenograft models. SJSA-1 cells, which exhibit high endosialin levels, were used to evaluate the therapeutic potential of ENDOS/ADC. The study demonstrated that the antibody component of ENDOS/ADC, hMP-E-8.3, efficiently binds and internalizes into SJSA-1 cells, facilitating targeted drug delivery. In vitro experiments showed that ENDOS/ADC treatment induced significant cytotoxicity in SJSA-1 cells while sparing endosialin-deficient counterparts, confirming its specificity. In vivo studies further validated ENDOS/ADC’s effectiveness, leading to sustained tumor regression in SJSA-1 xenografts, with some cases achieving complete remission. The treatment was well-tolerated, with no significant toxicity observed in mice. These findings highlight SJSA-1 xenografts as a valuable preclinical model for testing endosialin-targeted therapies and support the further development of ENDOS/ADC as a promising therapeutic strategy for osteosarcoma and other endosialin-expressing tumors.
The Role of SJSA-1 in Targeted Cancer Therapy Studies
SJSA-1 is a human osteosarcoma cell line characterized by wild-type TP53 and high levels of MDM2 amplification. This overexpression of MDM2 leads to the suppression of p53 function, reducing apoptosis and promoting tumor survival. As a result, SJSA-1 is widely used in cancer research to study the effects of MDM2 inhibitors, such as Nutlin-3 and RG7388, which aim to restore p53 activity. Additionally, this cell line harbors an NRASQ61K mutation, making it a suitable model for investigating MAPK pathway inhibitors, including trametinib. Studies show that while SJSA-1 cells undergo growth arrest in response to these inhibitors, they exhibit minimal apoptosis due to persistent p53 suppression. This unique oncogenic profile makes SJSA-1 valuable for testing targeted therapies and understanding resistance mechanisms in osteosarcoma.
MDM2 Amplification and p53 Mutations: Driving Factors in SJSA-1 Osteosarcoma
SJSA-1 osteosarcoma cells are characterized by MDM2 amplification, which inhibits the tumor suppressor protein p53. This oncogenic mechanism allows unchecked cell proliferation by degrading p53, preventing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. While wild-type TP53 is initially present, exposure to MDM2 inhibitors can select for TP53 mutations, leading to drug resistance. These mutations disrupt p53’s ability to activate its target genes, further enhancing tumor survival. Despite resistance to MDM2 inhibitors, TP53-mutant SJSA-1 cells remain sensitive to ionizing radiation, suggesting alternative therapeutic options.
Xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of drugs against specific types of cancer. New medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels).
Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC-regulated and GLP compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis).
Following options are available for the SJSA-1 xenograft model:
- SJSA-1 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- SJSA-1 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- SJSA-1 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cisplatin, at a dosage of 35-40 mg/kg
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging, MRI
