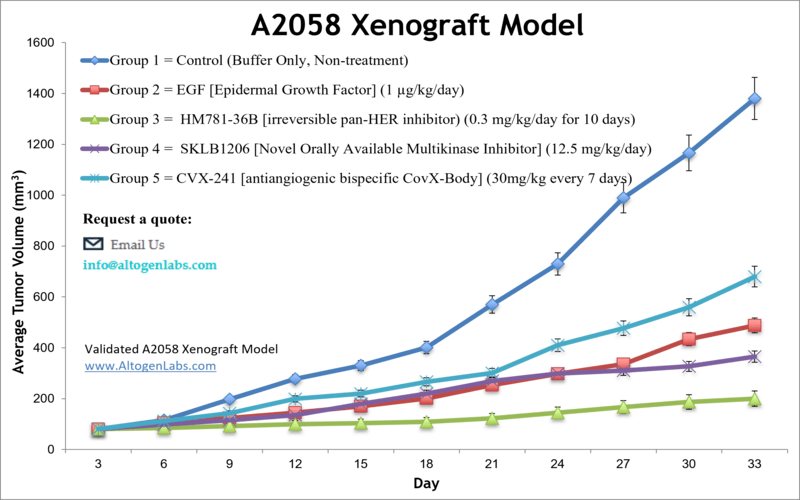
A2058 xenograft model (subcutaneous and metastatic)
The A2058 cell line is a human melanoma cell line that was derived from a lymph node metastasis of a patient with malignant melanoma. A2058 cells are commonly used in cancer research to study the biology of melanoma and test new therapies. The incidence of malignant melanoma, a highly metastatic form of cancer, is increasing globally at a dramatic rate. Due to limited therapeutic options for patients with late-stage melanoma, innovative treatment regimens are desperately needed. The A2058 cell line was established from a lymph node metastasis of a 43-year-old male patient with malignant melanoma. PCTAIRE1/CDK16/PCTK1 plays an invaluable role in cancer cell proliferation and is overexpressed in various human tumors, including malignant melanomas. A 2016 study by Yanagi et al. published in Molecular Therapy-Nucleic Acids investigated the in vivo therapeutic potential of treatment with PCTAIRE1 siRNA-lipid nanoparticles using the A2058 xenograft model of human melanoma. These findings indicate that siRNA treatment targeting PCTAIRE1 is effective in vivo and suggest that PCTAIRE1 siRNA-lipid nanoparticles could be a new therapeutic approach for melanoma patients. A 2012 study by Tian et al. used the A2058 cell model to evaluate a series of spirooxindole derivatives (SOID 1-12) and their effects on melanoma, a disease that is often refractory to available chemotherapies. Results demonstrated that SOID-8 decreased STAT3 and JAK2 phosphorylation, ultimately resulting in apoptosis induction and in vivo tumor growth suppression. In 2011, Rozenberg et al. released a study evaluating metastases in orthotopic murine skin cancer models, including the A2058 xenograft model. Ultimately they concluded data supported a model of melanoma metastasis where ERK activation and epidermal-to-mesenchymal (EMT) transition may facilitate metastasis but may not be a prerequisite as previously believed. Finally, a study by Hoeflich et al. (2011) used the A2058 model to evaluate a novel MEK and PI3K inhibition combination therapy. They used GDC-0973 (MEK inhibitor) and GDC-0941 (PI3K inhibitor); results showed that continuous combination exposure was not required and that intermittent dosing was just as effective. The CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) A2058 xenograft mouse model is created from the A2058 cell line (human melanoma). This cell line can be utilized for in vivo melanoma therapeutic studies specific for increased pERK and pAKT status.
Download Altogen Labs A2058 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- The A2058 cells are cultured under conditions of exponential growth prior to injection.
- The cells are trypsinized and, using a flow cytometry (Guava) or trypan blue exclusion assay, viable cell counts are determined (98% cell viability required). The cell suspension is then adjusted to the appropriate density needed for inoculation.
- The mice (athymic BALB/c nu/nu, ~8-9 weeks old) receive the subcutaneous injection into the flank of the hind leg. The injection contains one million cells (in a volume of 100-150µL) of the Matrigel and A2058 cell suspension.
- Injection sites are palpated up to three times weekly until tumors are established. The tumors are measured using digital calipers and monitored until they reach 100-150 mm3.
- Animals are randomized into treatment cohorts and administration of compound of interest is performed according to the treatment schedule
- Mouse weights are recorded 2-3 times weekly and tumors are measured daily.
- The animals are euthanized at the experimental determined limit or when tumor size reaches 2,000 mm3 or size determined by approved IACUC protocol.
- Necropsy and tissue collection is performed as defined for termination of experiment.
- The tumors are excised from the animals, weighed and then documented by digital imaging.
- Gross necropsies are performed and customer specified tissues are collected for downstream analysis.
- Tumors or tissues can be snap frozen in LN2, stabilized in RNAlater or prepared for histology.
Metastatic Model
CDX models are mouse xenografts used in pre-clinical therapeutic studies. However, as primary tumors proliferate they invade surrounding tissue, become circulatory, survive in circulation, implant in foreign parenchyma and proliferate in the distant tissue. This result leads to an extremely high percentage of death in cancer patients due to metastasis. Metastatic tumor mouse models are utilized to develop novel therapeutic agents that target metastasis (anti-metastatic therapeutics).
To create a metastatic model, the cell line of interest is transfected with vectors containing green fluorescent protein (GFP) or luciferase. Maintained under antibiotic selection, only cells containing the integrated vector will survive. The new cell line clones are capable of stably expressing the gene of interest and are used in metastatic mouse model studies. Although each new cell line clone may contain its own inherent difficulties, the new cell line contains the ability to track internal tumor progression via bioluminescence (luciferase fluorescence after injecting luciferin) or fluorescence (GFP). Internal orthotopic and metastatic tumor growth (not palpable) can now be measured throughout the study, enabling a researcher to gain more insight and additional data in contrast to relying on end of study tumor weight measurements.
Case Study: U87-luc Xenograft Model
An example of Altogen Labs utilizing a luciferase expressing cell line to monitor orthotopic tumor growth is exhibited below. The same ideology of tumor observation is incorporated in metastatic tumor models.
Luciferase expressing U87-luc cells were implanted and tumors allowed to grow. Tumor growth was monitored in a Night Owl (Berthold Technologies) imaging system 10 minutes after an intraperitoneal (IP) injection of the luciferin substrate. As seen in the example below, luciferase expression (measured as photons emitted) in the U87-luc model grants the researcher a visual image and quantifiable metric for orthotopic or metastatic tumor progression.
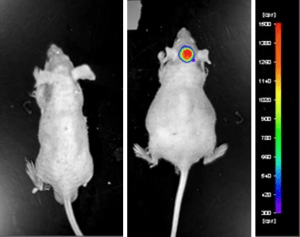
Figure 1. Luciferase expression in U87-luc orthotopic model. Control and implanted glioma mouse model fluorescence was analyzed 10 minutes after intraperitoneal luciferin injection.
View full details of the case study by clicking here.
Get Instant Quote for
A2058 Xenograft Model
The dosing of the experimental compound of interest is initiated, for a staged study, when the mean tumor size reaches a specified volume (typically 50-100 mm3). In an unstaged study, the dosing of the compound of interest is initiated immediately after xenografting. Mice are dosed once or twice a day for 28 days (or other desired study duration) via the chosen route of administration. Tumor volume (mm3) is calculated via the “(W x W x L) / 2” formula, where W is tumor width and L is tumor length. Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC regulated and GLP compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression.
Following options are available for the A2058 xenograft model:
- A2058 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- A2058 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- A2058 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 25 mg/kg administered by intramuscular injection to the control group daily for the study duration
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
