KARPAS-299 xenograft model
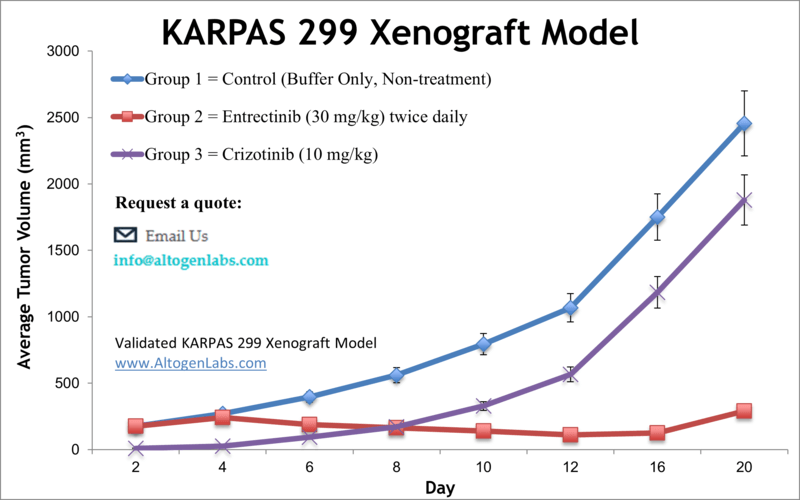
KARPAS 299 is a human T-cell lymphoma cell line that was originally derived from the lymph node of a patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. These cells have been widely used as a model system for studying various aspects of lymphoma biology, including the molecular mechanisms underlying lymphoma development and progression, and the identification of potential therapeutic targets for the treatment of lymphoma. KARPAS 299 cells have several properties that make them useful for research. Firstly, they are relatively easy to culture in the laboratory and can be grown in large quantities. Secondly, they express markers of T-cell lymphoma, such as CD2, CD3, and CD7, and exhibit several features characteristic of lymphoma, including uncontrolled proliferation and survival. Thirdly, they respond to various stimuli, such as cytokines and growth factors, making them a useful model system for studying the effects of these factors on lymphoma cell growth and survival. Non-Hodgkin lymphoma is cancer that originates in lymphocytes. It often affects patients age 65 or older, accounting for roughly 4 percent of all malignancies in the United States, as per the American Cancer Society. Anaplastic large cell lymphoma (ALCL) is an aggressive subtype of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. The KARPAS299 cells represent a human lymphoma cell line isolated from the peripheral blood of a 25-year-old male patient with non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. KARPAS 299 is a reliable tool in oncology research. A 2017 study by Xu et al. published in Cancer Research and Treatment investigated the combined anti-proliferative effects of everolimus and crizotinib in ALK-positive ALCL cell line Karpas 299 as well as in the Karpas 299 xenograft model. The article reports that both everolimus and crizotinib inhibits cell growth in a dose-dependent manner and the combination treatment of crizotinib and everolimus has a stronger antitumor effect than monotherapies in vivo, which indicates that crizotinib combined with everolimus inhibits proliferation of ALK-positive lymphoma cells and could be beneficial for ALCL patients. A 2014 Nature Biotechnology by Lyon et al. article used the Karpas 299 xenograft model to investigate the inhibiting stability of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) which have a reactive thiol group conjugated to maleimide-containing components. The group used diaminopropionic acid (DPR) to incorporate a basic amino group next to the maleimide so that a thiosuccinimide ring hydrolysis would occur, which prevents further elimination reactions and nonspecific deconjugation. They used the Karpas xenograft model to demonstrate that ADCs with the DPR group have improved stability and antitumor activity. A Clinical Cancer Research article by Numbenjapon et al. (2009) used the Karpas 299 model in their preclinical study looking into their developed analog of camptothecin. Camptothecin (CPT) is a type 1 DNA topoisomerase inhibitor that is too toxic to use clinically and CPT-11 is the more classically used water-soluble and minimally toxic analog of CPT, but with diminished activity. This group’s analogue (IT-101) is a polymer conjugate of 20-S-CPT and cyclodextrin-based and demonstrated high in vitro cytotoxicity and prolonged survival in vivo. Finally, another 2009 Clinical Cancer Research study (Cardarelli et al.) used the Karpas 299 model, in this case to characterize MDX-1401, the human nonfucosylated monoclonal antibody against CD30 (of the tumor necrosis factor superfamily). MDX-1401 showed higher antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) as compared to its parent antibody and was successful in preventing tumor growth in the CD30 positive Karpas299 xenograft model. The KARPAS 299 cell line (human lymphoma) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) KARPAS 299 xenograft mouse model. The KARPAS 299 xenograft model, a CD30+ cell line, allows for antibody drug conjugate testing (such as MMAE conjugated to anti-CD30).
Download Altogen Labs KARPAS299 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- The cells, maintained at exponential growth, are collected for inoculation by trypsinization. Viability and cell counts are determined by using trypan blue (98% min viability).
- The KARPAS 299 cell suspension concentration is adjusted to the density needed for inoculation.
- In a volume of 100 µL, one million cells (Matrigel+KARPAS-299 cells suspension) is injected into hind leg flank of each mouse (NOD/SCID or athymic BALB/C, 10 to 12 weeks) subcutaneously (s.c).
- Calipers are used to measure tumors; average sizes of 50-150 mm3allow the animals to be sorted into the treatment cohorts.
- Administration of test materials are given according to the treatment schedule. Tumor measurements are recorded daily; mouse weights are recorded 2 times weekly.
- At the study’s tumor size limit, animals are euthanized and a necropsy is performed. Tumors are removed, weight recorded and tumor documented (digital imaging).
- Collected tissues, by standard necropsy, can be: snap frozen in liquid nitrogen submersed with RNAlater reagent, isolated nucleic acids or prepared for histology.
Get Instant Quote for
KARPAS 299 Xenograft Model
Researchers investigating the role of specific proteins or gene products in regulating tumor growth can benefit from development of protein overexpression (genetically engineered to ectopically express proteins, tumor suppressors, or oncogenes) and RNAi cell lines with long term gene silencing. Altogen Labs provides quantitative gene expression analysis of mRNA expression (qPCR) and protein expression analysis using the WES system. Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC regulated and GLP compliant. Following acclimatization to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Our animal facilities have the flexibility to use specialized food or water systems for inducible gene expression systems.
Following options are available for the KARPAS 299 xenograft model:
- KARPAS 299 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- KARPAS 299 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- KARPAS 299 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
