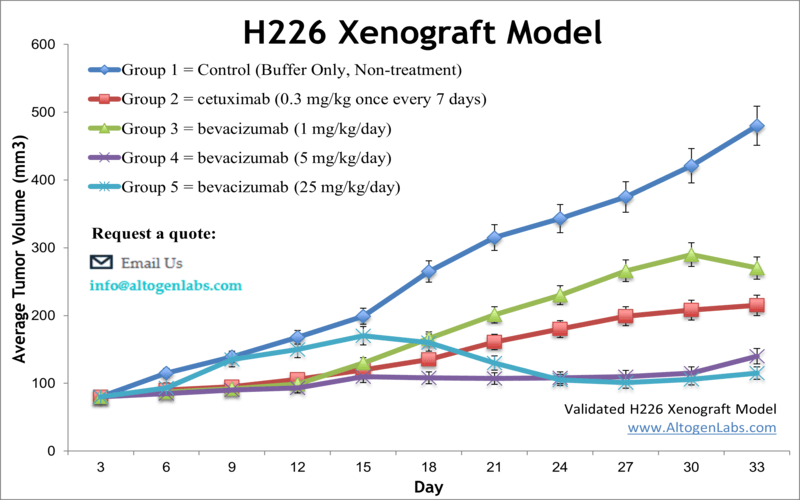
H226 xenograft model
Lung cancer is the primary cause of cancer fatalities in both men and women, accounting for 14 percent of all new cancer diagnoses. It is responsible for 1 in 4 cancer deaths with the 5-year survival rate of only 18 percent, as stated by the American Cancer Society. The NCI-H226 mesothelioma cell line is derived initially from the pleural fluid of a patient with mesothelioma. NCI-H226 cells are essential in lung cancer research for assessing cytotoxic effects of therapeutic agents. A 2017 study by Lam et al. published in Respiratory Research investigated the effects of pegylated arginase (PEG-BCT-100) in malignant pleural mesothelioma (MPM). The article reported that pegylated arginase suppresses tumor growth mediated by intratumoral arginine depletion and results in apoptosis and G1 arrest in the H226 mesothelioma xenograft model. These findings demonstrate scientific evidence supporting the further clinical development of BCT-100 in the treatment of MPM. A 2014 Clinical Cancer Research article by Huang et al. used the H226 xenograft model to investigate therapies targeting the Hedgehog (HH)-GLI signaling for treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma (LSCC). The group examined the inhibition of Smoothened (SMO) and GLI2 inhibition via small molecules GDC-0449 and GANT61, respectively, and results showed that inhibition of GLI2 demonstrated significant cytotoxicity in cells and antitumor activity in xenografts. This supports the inhibition of GLI2 for further study as a target against LSCC. Li et al. released a Molecular Cancer Therapeutics study (2015) using the H226 model to study the effects of inhibiting epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and human epidermal growth factor (HER3) with the dual-specific antibody MEHD7945A. Results demonstrated that in xenografts, treatment with MEHD7945A inhibited tumor growth and enhanced radiosensitivity (increased levels of γ-H2AX mediated double strand breaks) which promotes the investigation of this technique for clinical use of dual EGFR/HER3 inhibition as a radiation sensitizer. The NCI-H226 cell line (human lung) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) H226 xenograft mouse model. The H226 xenograft model is an excellent preclinical murine model for lung cancer to study chemosensitivities similar to the tissue of origin (e.g. irinotecan, doxorubicin, bevacizumab).
NCI-H226 Lung Cancer Xenograft Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs NCI-H226 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
EIF4G1 Regulates NCI-H226 Growth
EIF4G1 was found to be highly expressed in LSCC tissues and cell lines, including NCI-H226, and its overexpression correlated with poor patient prognosis. Functional assays demonstrated that silencing EIF4G1 in NCI-H226 cells significantly inhibited proliferation, colony formation, and cell cycle progression by inducing G1 phase arrest. Western blot analysis revealed that EIF4G1 regulates LSCC cell growth through the AKT/mTOR and Cyclin D1 pathways. In vivo, EIF4G1 knockdown suppressed tumor growth in xenograft models, supporting its role in LSCC tumorigenesis. This suggest that EIF4G1 acts as a key regulator of LSCC progression and could serve as a prognostic marker and therapeutic target, particularly in NCI-H226 cells. Further research is needed to explore the clinical potential of targeting EIF4G1 in LSCC treatment.
NSCLC Progression via ErbB4-Mediated PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 Activation
In a study by Yue A. et al., investigated the role of tastin in non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) progression using NCI-H226 squamous cell carcinoma cells. Tastin was found to be significantly overexpressed in NSCLC tissues, correlating with poor patient prognosis. Silencing tastin in NCI-H226 cells led to reduced proliferation, migration, and invasion capabilities. Mechanistically, tastin interacts with ErbB4, activating the PI3K/AKT and ERK1/2 signaling pathways that drive tumor growth. In vivo experiments with xenograft models confirmed that tastin knockdown suppressed tumor development. These findings highlight tastin as a potential therapeutic target for NSCLC. Overall, the study emphasizes the critical role of tastin in enhancing the malignancy of NCI-H226 lung cancer cells.
Inhibition of FGF/FGFR Pathway in NCI-H226 Mesothelioma Cells
Another study conducted by Blackwell C. et al, investigated the efficacy of GSK3052230, an FGF ligand trap, in inhibiting tumor growth in mesothelioma models. NCI-H226 mesothelioma cells, characterized by high FGF2 and FGFR1 expression, exhibited significant sensitivity to GSK3052230 treatment. In vivo, GSK3052230 notably suppressed tumor growth in NCI-H226 xenograft models, demonstrating dose-dependent tumor growth inhibition. The treatment effectively reduced MAPK pathway signaling, as evidenced by decreased phospho-ERK and phospho-S6 levels in both in vitro and in vivo settings. Additionally, GSK3052230 led to a significant reduction in tumor vessel density, indicating its impact on angiogenesis. The observed antitumor effects highlight the dependency of NCI-H226 xenografts on FGF/FGFR autocrine signaling. These findings support further clinical evaluation of GSK3052230 as a promising therapeutic strategy for mesothelioma.
Basic study design
- H226 cells are maintained under conditions of exponential growth phase prior to injection. The cells are then prepared for injection by trypsin-EDTA and viable cells are determined. Cell suspension is adjusted to a concentration of 1 x 106 cells per 150 microliters (cells + 50% matrigel solution).
- Athymic BALB/c Nude mice (10-12 week old) receive s.c. injections in the flank of one hind leg. The injection sites are palpated and monitored until tumors are established. At an average size of 100-150 mm3, animals are randomized into predetermined treatment cohorts. In-life administration of the compound of interest is applied following the treatment schedule.
- Mouse weights (2-3 times weekly) and daily tumors measurements are logged.
- Maximum tumor size (2,000 cubic millimeters) marks the end of the study, at which point a necropsy and tissue collections are performed. Tumors are excised and weighed (tumors are also imaged digitally).
- All samples can be snap frozen or prepared for histology by submersion in 10% NBF formalin.
Get Instant Quote for
NCI-H226 Xenograft Model
Xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of drugs against specific types of cancer. New medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels).
Altogen Labs provides an array of laboratory services using over 90 standard Cell Line Derived Xenograft (CDX) models and over 30 PDX models. Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facilities are IACUC-regulated and GLP-compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression.
Following options are available for the H226 xenograft model:
- H226 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- H226 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- H226 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 50 mg/kg administered by intramuscular injection to the control group daily for the study duration
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
