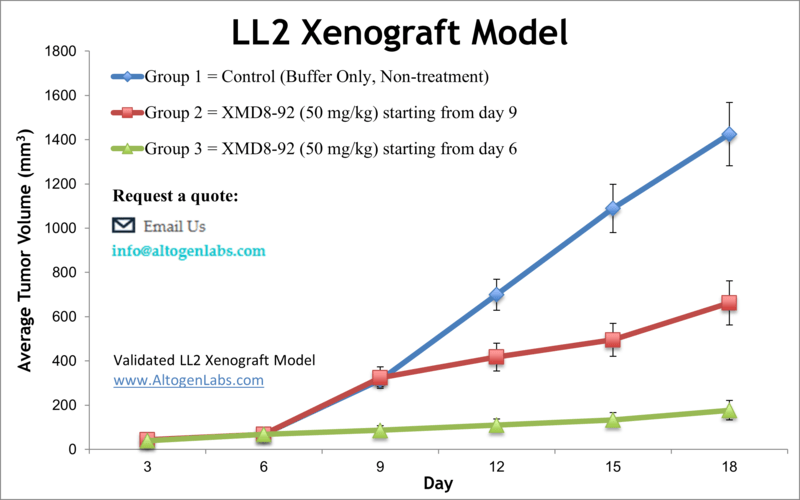
LL2 allograft model
LL2 (Lewis lung carcinoma 2) cells are a mouse cancer cell line that was originally derived from a spontaneously arising tumor in a mouse strain with high susceptibility to lung tumors, known as the C57BL/6J mouse strain. LL2 cells have been widely used as a model system for studying lung cancer biology, particularly in the context of immunotherapy and the tumor microenvironment. LL2 cells express markers of lung cancer, such as carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) and cytokeratin, and exhibit several features characteristic of lung cancer, including uncontrolled proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Thirdly, they respond to various stimuli, such as cytokines and chemokines, making them a useful model system for studying the effects of these factors on lung cancer cell growth and survival.
Lung cancer is the most preventable malignancy globally. However, it is the deadliest form of cancer with very high mortality rates. Murine models are instrumental in nonclinical research for studying novel therapeutic agents and treating human cancer. The tumorigenic and weakly metastatic LL/2 cell line was isolated in 1985 from tumor cells of a mouse with a Lewis lung carcinoma. The cells are hypotetraploid, have a 72 modal chromosome number (Dus et al.). A 2010 study by Yang et al. published in Cancer Cell investigated the BMK-mediated inhibition of the tumor suppressor activity of promyelocytic leukemia protein (PML) in tumor cells. A small-molecule inhibitor of the kinase activity of BMK1, XMD8-92, blocks tumor cell proliferation in vitro and significantly inhibits tumor growth in the LL/2 allograft model in vivo, demonstrating the efficacy and tolerability of BMK1-targeted cancer treatment in mice. A 2018 study by Chen et al. used the LL/2 allograft model to analyze the effects of a protein-bound polysaccharide (antrodan) derived from fungal mycelia of Antrodia cinnamomea when combined with Cisplatin. Results showed that this combination treatment had a number of positive results including: inhibition of plasma urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), inhibition of p38 and ERK2, decreased kidney dysfunction induced by cisplatin (decreased blood urea nitrogen (BUN)), reduced signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3), inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs) and JNK and an immunomodulation-mediated anti-metastasis response. Finally, a 2012 study in Journal of Cancer by Yan et al. used LL/2 cells to examine toxicity of curcumin, an anti-inflammatory agent, on lung carcinoma. It has been reported that curcumin exhibits phototoxicity and selectively kills tumor cells; this study confirmed this phenomenon and was the first to show that curcumin treatment results in subpopulations with minimized aggression. The LL/2 cell line (mouse lung; Lewis lung carcinoma) is used to create the CDX LL/2 allograft model. The LL/2 allograft model, known to be resistant to BCNU, enables anti-tumor growth studies such as those studying inhibitors of BMK1 (e.g. XMD8-92).
LL2 Lung Cancer Allograft Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs LL2 Allograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
LL2 Orthotopic Model for Lung Cancer Progression and Metastasis
Implanting LL/2 tumor cells into the lungs of immunocompromised mice allows for interactions between the tumor and the surrounding lung stroma, which affects tumor growth, differentiation, and drug sensitivity. From this, LL/2 cells can metastasize to distant organs, with patterns of spread resembling those seen in human lung cancer. This makes the LL/2 orthotopic model particularly valuable for studying lung cancer progression and evaluating potential therapeutic agents in a more biologically relevant context. However, the metastasis in LL/2 models is often highly heterogeneous, with variability in the spread and development of secondary tumors. Despite this, the LL/2 orthotopic model is able to provide key insights into tumor behavior and the interactions between cancer cells and their microenvironment.
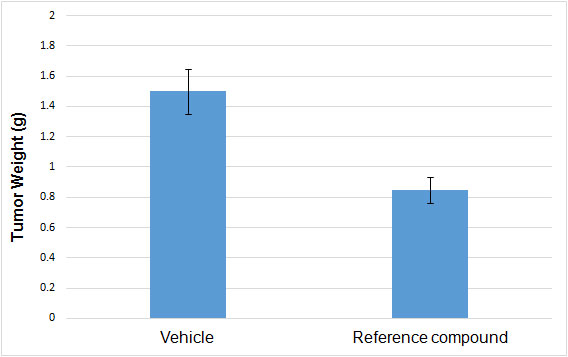
Tumorigenicity and Metastasis of LL2 Cells in Mice
LL/2 cells are known for their high tumorigenicity, meaning they can readily form tumors when implanted into either immunocompromised or syngeneic C57BL/6 mice. While these tumors can metastasize, the cells exhibit relatively low metastatic potential in regular mice, with metastatic spread being limited compared to more aggressive cancer cell lines. Additionally, they have also been described as weakly responsive to checkpoint blockade immunotherapy, making them less effective for studying the full potential of immune checkpoint inhibitors in promoting anti-tumor immunity. These limitations suggests that additional therapies or models might be necessary to explore immune checkpoint therapy more comprehensively. Regardless, LL/2 cells are commonly used in preclinical cancer research, especially in the context of tumor growth and immunotherapy evaluation.
Genomic Insights into LL2 Model Highlight Its Relevance for Cancer Therapy
Whole-exome sequencing of LL/2 reveals it as a hypermutated KRAS/NRAS-mutant cancer with extensive regional mutation clusters caused by chromosomal instability and frequent structural rearrangements. The LL/2 genome harbors over 20,000 somatic mutations, including 33 deleterious mutations in key cancer genes such as KRAS, NRAS, and Trp53, with biallelic deletions in Cdkn2a and Cdkn2b. This mutation profile suggests LL/2 shares molecular similarities with human lung adenocarcinoma, making it a valuable model for studying lung cancer progression and response to therapy. Additionally, LL/2 is known for its aggressive growth, high vascularization, and metastatic potential, particularly to the lungs, lymph nodes, and liver. The model’s syngeneic nature allows for immune-competent studies, enabling the evaluation of immune responses and targeted therapies. Its genomic characterization provides a foundation for its continued use in drug development, particularly in testing chemotherapeutics and immunotherapies.
Basic study design
- All tissue culture flasks are maintained aseptically at exponential cell growth. LL/2 cells are collected with trypsin-EDTA. Percentage of viable cells is determined via trypan blue exclusion.
- In a volume of 100 µL, 1 x 106 cells (Matrigel plus LL/2 cells suspension) are subcutaneously injected into C57BL mice (10-12 weeks old). Injection site tumor development is continually monitored and digital calipers are utilized until tumors reach 50-150 mm3.
- Test compounds are administered to the study groups following the dosing schedule. Daily tumor measurements are logged and mouse body weights recorded 3 times a week.
- Maximum tumor size limits marks the end of the in-life portion of the study. As defined in the study design, a necropsy is performed. Tumor excision and weights are documented and then imaged. At the client’s instruction, tissues can be fixed in 10% NBF, snap frozen or stabilized in RNAlater.
Get Instant Quote for
LL/2 Allograft Model
Xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of experimental test compounds against specific types of cancer. New medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised NOD/SCID mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels). Altogen Labs provides an array of laboratory services using over 90 standard Cell Line Derived Xenograft (CDX) models and over 30 PDX models. Researchers investigating the role of specific proteins or gene products in regulating tumor growth can benefit from development of protein overexpression (genetically engineered to ectopically express proteins, tumor suppressors, or oncogenes) and RNAi cell lines with long term gene silencing. Altogen Labs provides quantitative gene expression analysis of mRNA expression (RT-PCR) and protein expression analysis using the WES system (ProteinSimple). The dosing of the experimental compound of interest is initiated, for a staged study, when the mean tumor size reaches a specified volume (typically 80-100 cubic mm).
Following options are available for the LL2 allograft model:
- LL/2 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- LL/2 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- LL/2 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 30-50 mg/kg
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
