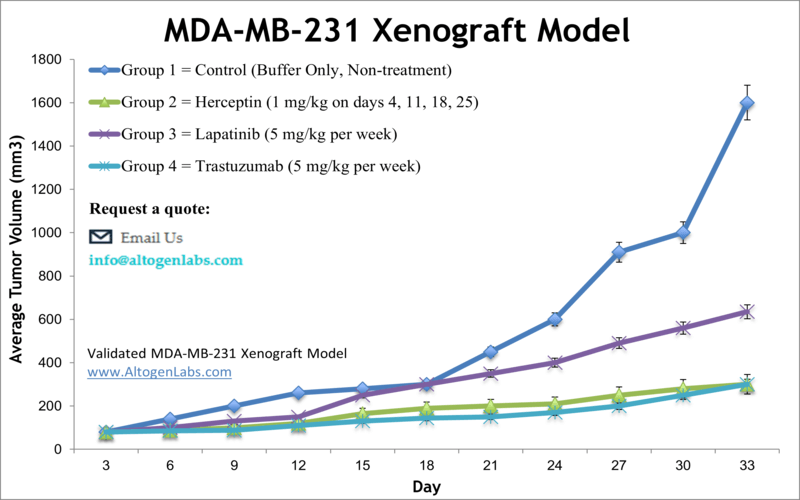
MDA-MB-231 xenograft model
MDA-MB-231 cells have several properties that make them useful for research. Firstly, they are relatively easy to culture in the laboratory and can be grown in large quantities. Secondly, they express markers of breast cancer, such as estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and HER2, and exhibit several features characteristic of breast cancer, including uncontrolled proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Thirdly, they respond to various stimuli, such as cytokines and growth factors, making them a useful model system for studying the effects of these factors on breast cancer cell growth and survival.
Breast cancer is the most prevalent form of cancer among American women, and has the second highest mortality rate in females after lung cancer. The MDA-MB-231 epithelial triple negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line is isolated from a 51-year-old Caucasian female with a metastatic mammary adenocarcinoma and is very widely-used in cancer research laboratories. The MDA-MB-231 cell line is ER-negative with an invasive phenotype an appearance of spindle-shaped cells. According to the study published in Breast Disease Journal, the TNBC cell lines are extremely aggressive and mirror the original tumors, making them powerful tools for investigative breast cancer research using MDA-MB-231 xenograft model. The MDA-MB-231 cell line is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) MDA-MB-231 xenograft mouse model. The MDA-MB-231 xenograft model is HER2 negative, CK18 and EGFR positive and exhibits tumor growth inhibition from herceptin, lapatinib and trastuzumab.
Research that has used these cells include the study by Iorns et al. (2012) that examined the MDA-MB-231 xenograft mouse model to determine the expression changes that occur when breast cancer cells metastasize to from the mammary pad primary tumor to distant organs. They found that the tumor cells had several changes in gene expression that suggests its necessity for successful metastasis and secondary organ tumor growth. A 2008 study by Radestock et al. selected the MDA-MB-231 xenograft model to study the effects of relaxin on tumor cells in an oestrogen receptor alpha-negative system. Relaxin overexpression was previously associated with promotion of migration however this study identified a novel mechanism of action where long-term relaxin expression leads inhibition of growth and invasion of breast cancer cells through the down-regulation of S100A4 (metastasin), a promotor of metastasis linked to poor prognosis in cancer patients. Finally, a 2016 Nature study (Wang et al.) used the MDA-MB-231 xenograft model to investigate the mechanism of action of SL4, a compound known to slow tumor invasion and angiogenesis. They report that SL4 inhibits proliferation through cell cycle arrest with clinically relevant IC50 values and apparent toxicity.
MDA-MB-231 Orthotopic And Metastatic Xenograft Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs MDA-MB-231 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Orthotopic MDA-MB-231 Model
The orthotopic MDA-MB-231 model involves the implantation of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells into the mammary fat pad of immunocompromised mice, closely mimicking the natural environment of breast cancer growth. This model is commonly used to study the tumor microenvironment, tumor growth, and metastasis, as the cells maintain key characteristics of the primary tumor, such as invasiveness and hormone receptor-negative status. By injecting cells suspended in Matrigel, researchers can observe the development of both local and distant metastases, such as lung, liver, and lymph node involvement. The orthotopic MDA-MB-231 model is especially valuable for testing therapies targeting primary tumors and metastatic disease, as it replicates key aspects of human breast cancer. Tumor growth is monitored regularly by calipering, and metastasis is assessed using imaging techniques or histological analysis. This model is widely used in drug discovery and for understanding the mechanisms of cancer progression. The ability to study both the primary tumor and its metastases in a relevant, physiological context makes the orthotopic MDA-MB-231 model an essential tool in preclinical cancer research.
Evaluating Metastatic Breast Cancer Progression Using MDA-MB-231
The metastatic MDA-MB-231 model involves injecting MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells into immunocompromised mice, allowing researchers to study the full metastatic process, from primary tumor growth to distant organ spread. This model is particularly useful for studying triple-negative breast cancer, as MDA-MB-231 cells lack estrogen, progesterone, and HER2 receptors, making them highly aggressive and prone to metastasis. Once injected, the cells form primary tumors in the mammary fat pad, and metastasis is monitored in organs such as the lungs, liver, and lymph nodes. Researchers can assess tumor growth, metastasis, and response to therapeutic interventions using imaging techniques, histology, and molecular markers. The metastatic MDA-MB-231 model is a valuable preclinical tool for evaluating treatments aimed at preventing or treating metastatic breast cancer. It helps in understanding the molecular mechanisms driving metastasis, such as epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) and angiogenesis. This model is frequently used in drug discovery, particularly for developing therapies targeting both the primary tumor and metastatic sites. The ability to observe the entire metastatic cascade in a relevant biological context makes it an indispensable model in cancer research.
Sphingosine Kinase Activity for MDA-MB-231 Survival
A study conducted by Rex K, et al. published by PLOS One journal, investigates whether sphingosine kinase (SPHK) activity is essential for the viability of MDA-MB-231, a triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line, and other tumor cells. SPHKs produce sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P), a signaling lipid implicated in cell survival, proliferation, and tumor progression. The rheostat theory suggests that SPHK activity shifts the balance from pro-apoptotic sphingolipids to mitogenic S1P, thereby promoting cancer cell survival. Using SPHK1/2 inhibitors, researchers successfully blocked intracellular S1P production in MDA-MB-231 and other cell lines. Surprisingly, this did not lead to a reduction in cell viability in vitro or tumor growth in vivo. Further validation using siRNA knockdown of SPHK1 and SPHK2 in multiple tumor cell lines, including MDA-MB-231, failed to show significant effects on viability, contradicting the expected role of SPHK in apoptosis regulation. In xenograft models, MDA-MB-231 tumors in mice continued to grow despite SPHK inhibition, while positive controls like Docetaxel effectively suppressed tumor growth. Additionally, vascular permeability assays confirmed that SPHK inhibition influenced angiogenesis-related pathways but not direct tumor cell viability. The findings suggest that SPHKs are not essential for MDA-MB-231 cell survival, challenging their validity as therapeutic targets in oncology.
Chemotherapies: Foretinib Suppresses MDA-MB-231 Triple-Negative Breast Cancer Growth
Foretinib, a small-molecule kinase inhibitor, shows significant potential in treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) by targeting MDA-MB-231 cells. TNBC is a highly aggressive subtype with limited treatment options, often driven by overactive p-MET/HGF signaling. This study demonstrates that foretinib effectively inhibits tumor growth both in vitro and in vivo by downregulating phosphorylated MET (p-MET) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF), which are crucial for cancer cell proliferation and metastasis. In a mouse xenograft model, foretinib administration resulted in a dose-dependent reduction in tumor size without significant toxicity. Western blot and immunohistochemical analyses confirmed a decrease in p-MET and HGF expression, indicating that MET inhibition is a viable therapeutic strategy for TNBC. Additionally, pharmacokinetic analysis revealed that foretinib is rapidly metabolized, supporting its potential as a well-tolerated treatment. These findings suggest that targeting the MET pathway with foretinib could provide an effective therapeutic avenue for patients with TNBC, especially those with MET-overexpressing tumors.
Targeting Cancer Stem Cells in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer
Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) remains a difficult-to-treat subtype, often driven by aggressive cancer stem cells (CSCs). In a study by Tanei, T., et al., published by Breast Cancer Research journal, researchers investigated the effects of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR)-targeting monoclonal antibody Cetuximab, alone and in combination with Ixabepilone, in TNBC models using the MDA-MB-231 and SUM159 cell lines. Cetuximab effectively reduced the CSC population in both cell lines, as indicated by decreases in CD44+/CD24-/low and Aldefluor+ cells, key markers of stemness. Additionally, the study found that Cetuximab inhibited autophagy-related survival mechanisms in CSCs, further limiting their ability to regenerate. However, while Cetuximab alone showed promise, the combination therapy with Ixabepilone yielded significant improvements in tumor growth suppression only in SUM159 tumors, but not in MDA-MB-231 xenografts. These findings suggest that while targeting EGFR can impair CSC function, its therapeutic efficacy may be influenced by TNBC subtype-specific factors. The study underscores the importance of personalized treatment approaches in TNBC, as certain subpopulations, like MDA-MB-231, may require alternative or additional therapeutic strategies.
Get Instant Quote for
MDA-MB-231 Xenograft Model
Targeting Mitochondrial ncRNA to Halt Breast Cancer Growth
A novel approach to treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) focuses on targeting mitochondrial noncoding RNAs (ncmtRNAs) in MDA-MB-231 cells. Researchers found that knocking down specific antisense mitochondrial RNAs (ASncmtRNAs) triggers a powerful anti-cancer effect by inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. This mechanism works by downregulating key cell cycle proteins, including cyclin B1, cyclin D1, CDK1, CDK4, and survivin, which are essential for cancer cell proliferation. The treatment also increases specific microRNAs that further suppress these cell cycle regulators, amplifying the tumor-suppressive response. In a mouse xenograft model, this approach led to a significant reduction in tumor growth, demonstrating its potential as a therapeutic strategy. Importantly, this targeted intervention does not harm normal cells, making it a promising avenue for developing safer, more effective breast cancer treatments.
DEK Oncogene Knockdown Reduces Redox State and Invasiveness in MDA-MB-231 Cells
The DEK oncogene plays a significant role in the aggressiveness of MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells by influencing their redox state and invasive potential. DEK is a chromatin remodeling protein that is overexpressed in many cancers, including breast cancer, and is associated with increased proliferation, invasion, and metastasis. Optical redox imaging (ORI) studies have shown that MDA-MB-231 cells exhibit a high FAD redox ratio, correlating with their aggressive nature. When DEK expression is knocked down, these cells display a significantly lower redox ratio and reduced invasive potential, indicating that DEK contributes to metabolic reprogramming in cancer cells. DEK overexpression promotes an oxidized redox state, likely through its influence on mitochondrial metabolism and NAD-coupled redox balance. The study found that DEK knockdown reduced FAD fluorescence intensity and the FAD redox ratio, suggesting a shift toward a more reduced mitochondrial state. These findings further reinforce the link between oncogene activity and cellular metabolism in breast cancer. Given DEK’s role in tumor progression, it is considered a potential therapeutic target for inhibiting metastasis and improving treatment outcomes in triple-negative breast cancer.
Following options are available for the MDA-MB-231 xenograft model:
- MDA-MB-231 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- MDA-MB-231 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- MDA-MB-231 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 20-40 mg/kg administered by intramuscular injection to the control group daily for the study duration
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
