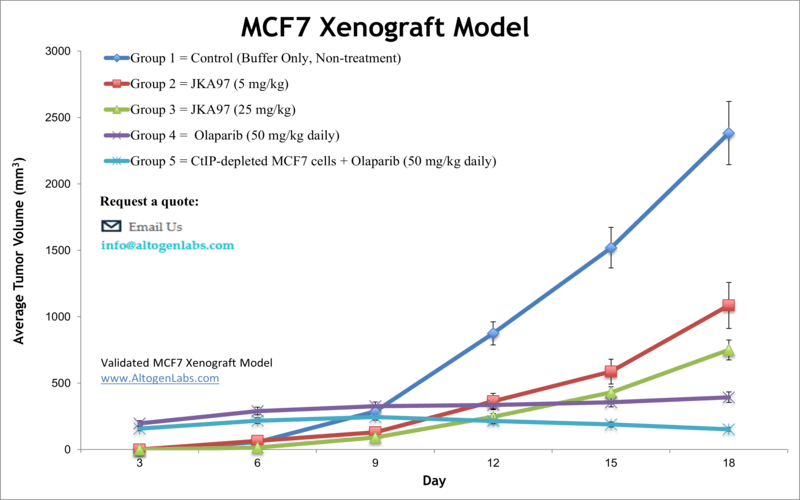
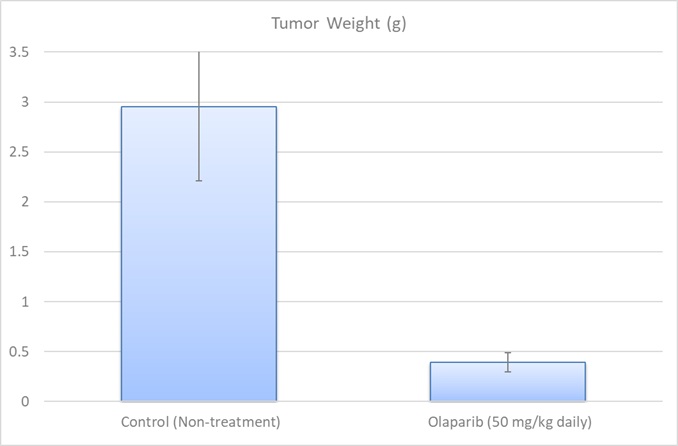
MCF7 xenograft model
Breast cancer represents a significant public health challenge due to it being the most prevalent malignancy in females. The MCF7 epithelial cell line was isolated from adenocarcinoma of the human breast of a 69-year-old Caucasian woman in 1970. The MCF-7 cell line expresses estrogen, progesterone and glucocorticoid receptors. MCF-7 has various characteristics of differentiated mammary epithelium such as the capability of forming domes or ability to process estradiol via cytoplasmic estrogen receptors and is the most well-characterized and widely used of all the human breast cancer cell lines. MCF7 stands for Michigan Cancer Foundation – 7, the institute where the cell line was established by Soule and associates. The MCF7 cell line is used to create the xenograft mouse model, however cells will not create tumors without supplementation and modified protocol. The MCF-7 xenograft model is positive expressing for the estrogen receptor (ER) and perpetuates studies to address cell death, apoptosis and mitotic arrest by chemotherapies (e.g. docetaxel). In MCF7 xenografts, MCF7 cells are typically injected into the mammary fat pad of immunodeficient mice. The resulting tumors exhibit many of the characteristics of human breast tumors, including uncontrolled proliferation, invasion, and angiogenesis. These tumors can be monitored over time by measuring their size using calipers, and can be harvested at different time points for further analysis. Examples of studies using the MCF7 xenograft model include the 2005 Clinical Cancer Research study (Brodie et al.) that explored combination therapy of tamoxifen with letrozole, a nonsteroidal aromatase inhibitor. They found that treating tumors with fulvestrant, an estrogen receptor agonist and antineoplastic agent, with letrozole was the most effective strategy for inhibiting tumor growth; the hypothesis was that tumor cells adapt to estrogen deprivation with letrazole treatment alone due to the increase in mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade levels of letrazole-resistant growths. A 2010 study (Fleming et al.) used a MCF7 xenograft to study mammary cancer mouse models and differences in tumor phenotype with varied microenvironments; they observed that DNA methylation status, vascularization and tumor growth/volume all varied depending on implantation technique (renal capsule, orthotopic, subcutaneous). Lastly, a 2008 study (Wu et al.) examined the effect of caveolin-1, a protein implicated in mitogenic signaling and oncogenesis, overexpression on MCF-7 xenograft mouse model; they presented novel in vivo evidence demonstrating the function of caveolin-1 as a tumor suppressor and not a tumor promoter as previously believed.
MCF7 Breast Cancer Subcutaneous And Orthotopic Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs MCF7 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Get Instant Quote for
MCF7 Xenograft Model
Orthotopic MCF7 Xenografts
The orthotopic MCF7 model is an advanced preclinical system used to study estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer in a physiologically relevant environment. In this model, MCF7 cells are implanted directly into the mammary fat pad of immunocompromised mice, allowing tumors to develop in their native tissue microenvironment. This approach better recapitulates the architecture, stromal interactions, and hormone responsiveness of human breast tumors compared to subcutaneous models. The orthotopic MCF7 model is particularly valuable for studying tumor progression, hormone-dependent growth, and response to endocrine therapies such as tamoxifen and aromatase inhibitors. Due to the relatively low metastatic potential of MCF7 cells, modifications such as genetic alterations or co-injection with stromal components are sometimes used to enhance invasion and metastasis. Additionally, this model enables investigations into the tumor microenvironment, including interactions with immune cells and the extracellular matrix.
Chemo-Endocrine Strategy Targeting ER-Positive MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells
A study conducted by Nukatsuka M, et al., explored the combined effects of the oral fluoropyrimidine S-1 and the estrogen receptor (ER) down-regulator fulvestrant on estrogen-responsive breast cancer, with a particular focus on the MCF7 cell line. MCF7, an ER-positive human breast cancer cell line, was used to evaluate cytotoxicity in vitro and in vivo. The results demonstrated that fulvestrant alone inhibited MCF7 cell growth but had no effect on the ER-negative MDA-MB-231 cells, highlighting its specificity for ER-positive tumors. When combined with 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in vitro, fulvestrant exhibited additive to supra-additive effects in inhibiting MCF7 cell proliferation. In vivo, S-1 and fulvestrant showed significantly greater tumor growth suppression in MCF7 xenografts compared to either monotherapy. Immunohistochemical analysis further revealed that fulvestrant partially downregulated ERα and progesterone receptor (PgR) expression, but in combination with S-1, it nearly abolished their presence. These findings suggest that the combination of S-1 and fulvestrant enhances antitumor efficacy by effectively reducing ERα-mediated signaling. Given that S-1 has a favorable toxicity profile and is an oral agent, this chemo-endocrine combination may provide an effective and convenient therapeutic strategy for postmenopausal patients with ER-positive breast cancer, warranting further clinical investigation.
MCF7 Breast Cancer Cells Respond to Continuous CDK4/6 Inhibition with G1T38
In another study by Bisi JE, et al., published by Oncotarget journal, researchers investigated the preclinical efficacy of G1T38, a novel and selective CDK4/6 inhibitor, in estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer, with a focus on the MCF-7 cell line. MCF-7, a well-characterized ER+ breast cancer model, was used for both in vitro and in vivo assessments of G1T38’s tumor-suppressive effects. The inhibitor demonstrated potent G1 cell cycle arrest and suppressed RB phosphorylation, a key event in CDK4/6-driven cancer proliferation. Compared to palbociclib, the first FDA-approved CDK4/6 inhibitor, G1T38 showed equivalent or superior tumor growth inhibition in MCF-7 xenografts while displaying improved pharmacokinetics, with higher tumor accumulation and reduced systemic exposure. Notably, continuous daily oral dosing of G1T38 was feasible without inducing severe neutropenia, a common adverse effect limiting current CDK4/6 inhibitors. Furthermore, G1T38 significantly enhanced tumor suppression when combined with endocrine therapies such as tamoxifen and fulvestrant, indicating strong synergy in hormone-dependent breast cancer models. The combination of G1T38 with PI3K inhibitors also yielded superior anti-tumor effects, highlighting its potential in overcoming therapy resistance. These findings establish G1T38 as a promising candidate for continuous, well-tolerated CDK4/6 inhibition in ER+ breast cancer, warranting further clinical evaluation.
The MCF-7 Cell Line: Unraveling ER+ Breast Cancer Mechanisms
Unlike more aggressive breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 cells exhibit low invasive potential, but they retain the ability to proliferate in response to estrogen stimulation. Due to their hormone sensitivity, MCF-7 cells are extensively used to evaluate the efficacy of endocrine therapies, including tamoxifen and fulvestrant, as well as novel CDK4/6 inhibitors. Additionally, these cells have been instrumental in studying the effects of environmental factors, such as alcohol exposure, on breast cancer progression, demonstrating ethanol-induced changes in gene expression, oncogenic markers, and stemness-related proteins. The ability of MCF-7 cells to form mammospheres also provides insight into cancer stem cell biology, helping researchers explore mechanisms of drug resistance and tumor recurrence. Given their genetic stability and responsiveness to hormonal and targeted therapies, MCF-7 cells remain a cornerstone of breast cancer research, drug discovery, and personalized medicine.
Lipid Regulation and Hormone Sensitivity in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells
MCF-7 is a widely used luminal A breast cancer cell line that expresses estrogen (ER) and progesterone receptors (PgR), making it a valuable model for studying hormone-responsive tumors. Unlike HER2-positive and triple-negative breast cancer cell lines, MCF-7 exhibits a distinct dependency on lipid metabolism, particularly cholesterol levels, which significantly impact its growth, proliferation, and gene expression. Studies have shown that cholesterol depletion reduces MCF-7 cell proliferation, downregulating Ki67, a marker of cellular proliferation, while simultaneously increasing ER and PgR expression. In contrast, high cholesterol levels enhance cell growth and suppress tumor-suppressive pathways, such as PTEN and CDKN1A. Additionally, cholesterol influences sphingomyelin metabolism, which is critical for maintaining membrane integrity and cell signaling, further affecting tumor progression. The modulation of cholesterol levels alters the expression of key regulatory enzymes, such as HMG-CoA reductase, which is upregulated under cholesterol-depleted conditions. These findings suggest that cholesterol plays a crucial role in breast cancer metabolism, therapeutic response, and potential drug resistance, highlighting the importance of lipid regulation in developing targeted cancer therapies.
Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facilities are IACUC-regulated and GLP-compliant. Following acclimatization to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression. Our animal facilities have the flexibility to use specialized food or water systems for inducible gene expression systems. Immunocompromised xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of experimental test compounds against specific types of cancer. Novel medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels).
Following options are available for the MCF7 xenograft model:
- MCF7 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- MCF7 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- MCF7 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, injection into the mammary fat pad)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
MCF7 Breast Cancer Subcutaneous And Orthotopic Model: Download ![]()
