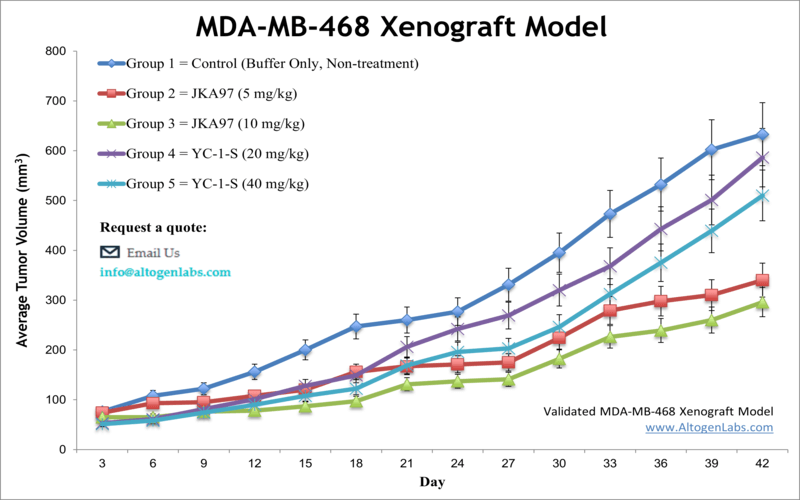
MDA-MB-468 xenograft model
MDA-MB-468 cells are characterized by their triple-negative status, cells do not express the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), or HER2. This subtype of breast cancer is associated with a poor prognosis and limited treatment options, making MDAMB468 cells an important tool for studying the molecular mechanisms underlying triple-negative breast cancer. Research using MDAMB468 cells has contributed significantly to our understanding of triple-negative breast cancer biology. The MDA-MB-468 cells have been used to study the role of various signaling pathways, such as the PI3K/Akt and MAPK pathways, in the development and progression of triple-negative breast cancer. Additionally, MDAMB468 cells have been used to screen for potential anticancer agents, including chemotherapy drugs and targeted therapies.
Breast cancer cell lines are invaluable models for a greater understanding of the genetic profile, molecular biosciences, biologic nuances and drug therapy development of the disease. Mouse xenograft studies routinely utilize cancer cell lines aiming to assess the efficacy of antitumor treatments. The MDA-MB-468 cell line was derived in 1977 by R. Cailleau from a pleural effusion of a 51-year-old female with breast adenocarcinoma. The MDA-MB-468 triple-negative cell line is commonly employed in oncology research for the study of metastasis and invasion of breast cancer. According to a 1994 study in Cancer Research, one of the main characteristics of the MDA-MB-468 cell line is the presence of a single p53 allele that harbors a point mutation at codon 273. A 2014 Cell Press article (Mason et al.) used the MDA-MB-468 model to identify CFI-400945, a polo-like kinase 4 (PLK4) inhibitor, as a candidate for clinical evaluation due to well-tolerated toxicity and inhibition of tumor growth via dysregulated mitosis and subsequent apoptosis. Hugo et al. released data in 2017 using MDA-MB-468 to demonstrate the oncogenic properties of E-cadherin, previously thought to be a tumor suppressor. Downregulation of E-cadherin had been associated with decreased proliferation and subsequent epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process necessary for metastasis; upon establishment of secondary metastases proliferation is restored via the reverse process of mesenchymal-to-epithelial transition (MET). This study presented findings suggesting the promotion of primary breast cancer cell growth and metastases formation by E-cadherin via supporting MET, effectively calling for a reevaluation of E-cadherin’s status as a tumor suppressor. A 2010 Clinical Cancer Research article (Bartholomeusz et al.) used a MDA-MB-231 xenograft model to establish the potential of PEA-15 as a therapeutic target; this group found that overexpression of PEA-15 inhibits tumorigenesis, reduces DNA synthesis and induces caspase-8-dependent apoptosis through increased intracellular levels of activated extracellular signal-regulated kinase. Finally, Kil et al. (2014) used the MDA-MB-468 xenograft model to verify that silibinin, a compound that inhibits tumor proliferation and induces cell cycle arrest, does have an anticancer effect on triple negative breast neoplasms; they reported the mechanism of action for silibinin effect is through preventing EGFR phosphorylation and suppressing expression of COX-2, VEGF AND MMP-9. The MDA-MB-468 cell line is used to create both subcutaneous and orthotopic xenograft mouse models. The MDA-MB-468 xenograft model is a triple negative model that can be used to study the efficacy of tumor growth inhibitors (e.g. silibinin, paclitaxel, PEA-15).
MDA-MB-468 Breast Cancer Tumor Model: Download ![]()
Download Altogen Labs MDA-MB-468 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
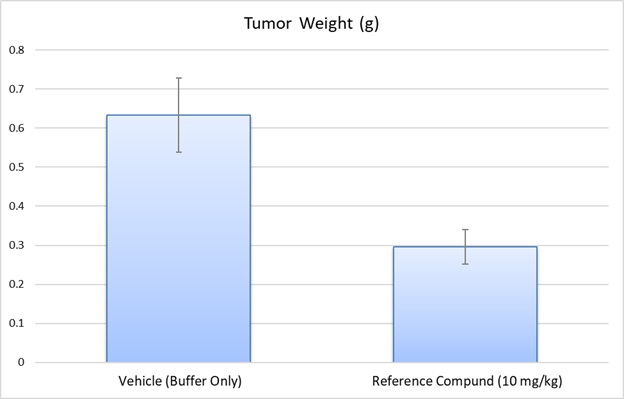
Orthotopic Implantation of MDA-MB-468 Cells in Cancer Research
The orthotopic MDA-MB-468 xenograft model involves the implantation of MDA-MB-468 cells into the mammary fat pad of immunocompromised mice, closely mimicking human breast cancer’s natural tumor microenvironment. This model is particularly valuable for studying the tumor’s growth, invasion, and metastasis, as it enables the observation of local and distant spread of cancer cells. Tumors develop within the mammary gland, providing more clinically relevant data on tumor behavior compared to subcutaneous models. The model is used to assess various therapeutic interventions, including chemotherapy, targeted therapies, and immunotherapy, allowing for evaluation of drug efficacy in a setting that reflects the complexity of human breast cancer. It is also crucial for studying cancer metastasis, as MDA-MB-468 cells exhibit the ability to spread to distant organs like the lungs and liver. This orthotopic model has contributed significantly to understanding the molecular mechanisms of tumor progression and metastasis in triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC).
Get Instant Quote for
MDA-MB-468 Xenograft Model
Enhanced Tumor Targeting with Anti-EGFR Nanobody-Conjugated Quantum-Dot Micelles
A study by Wang Y, et al., published by ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces journal, presents a quantum-dot (QD)-based theranostic micelle conjugated with an anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) nanobody (Nb) for targeted triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) therapy. The micelles, engineered with indium phosphate/zinc sulfide (InP/ZnS) QDs, enable both imaging and drug delivery. MDA-MB-468 cells, a TNBC cell line with high EGFR expression, played a central role in evaluating the micelles’ efficacy. The anti-EGFR nanobody, 7D12, significantly enhanced micelle uptake and cytotoxicity in MDA-MB-468 cells compared to non-targeted micelles. Encapsulation of the anticancer drug aminoflavone (AF) within Nb-conjugated micelles led to enhanced tumor accumulation and superior therapeutic efficacy in an orthotopic xenograft mouse model. Notably, targeted micelles demonstrated a 67-fold increase in cellular uptake in MDA-MB-468 cells and induced effective tumor regression, whereas non-targeted micelles had reduced efficacy. Importantly, treatment with the Nb-conjugated micelles showed no observable systemic toxicity, as indicated by stable body weight and normal histology of major organs. These findings highlight the potential of Nb-conjugated QD-based micelles as a promising platform for EGFR-overexpressing TNBC therapy.
Oncogenic Signaling and Therapeutic Targets in MDA-MB-468 Breast Cancer Cells
MDA-MB-468 is a triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line characterized by high expression of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and aggressive tumorigenic behavior. It harbors mutations in the PTEN gene, leading to dysregulation of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, which promotes cell survival and resistance to apoptosis. The PEA-15 phosphoprotein plays a critical role in MDA-MB-468 tumorigenesis by regulating ERK signaling; its overexpression sequesters phosphorylated ERK in the cytoplasm, reducing nuclear transcriptional activity and leading to growth inhibition. Additionally, c-Cbl, an E3 ubiquitin ligase, modulates EGFR degradation, but in MDA-MB-468 cells, its function is impaired, contributing to persistent EGFR signaling and uncontrolled proliferation. This cell line also exhibits dysregulated EZH2, a histone methyltransferase that drives epigenetic changes favoring tumor progression. Experimental therapies targeting these oncogenic drivers, such as enhancing c-Cbl-mediated degradation of EGFR or promoting PEA-15 overexpression, have shown promising tumor-suppressive effects in preclinical models.
Pharmacokinetics and Bystander Effects of T-DXd in MDA-MB-468 Tumors
MDA-MB-468 is a well-established triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line that expresses very low levels of HER2, making it an important model for evaluating the effectiveness of HER2-targeted therapies in tumors with minimal receptor expression. Unlike HER2-positive cell lines, MDA-MB-468 does not significantly accumulate trastuzumab-deruxtecan (T-DXd) payload, demonstrating a limited correlation between HER2 expression and drug exposure. Despite this, tumor growth inhibition was observed at higher T-DXd doses, suggesting alternative mechanisms, such as the bystander effect, may contribute to its cytotoxic activity. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic analyses reveal that MDA-MB-468 tumors exhibit lower levels of γH2AX and pRAD50, biomarkers of DNA damage response, compared to HER2-expressing tumors, indicating a less pronounced drug effect. Additionally, HER2 receptor quantification studies show that MDA-MB-468 harbors significantly fewer HER2 receptors per cell compared to HER2-positive models like NCI-N87, further explaining its reduced susceptibility to T-DXd. Despite its resistance to HER2-directed antibody-drug conjugates, MDA-MB-468 remains a valuable model for understanding drug distribution, payload release kinetics, and non-receptor-mediated cytotoxic effects. Future research using this model could refine dosing strategies and identify biomarkers predictive of ADC efficacy in HER2-low or negative tumors.
Metabolic Insights into MDA-MB-468: A Model for TNBC Metabolism
MDA-MB-468 is a widely used triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) cell line that serves as a model for studying metabolic adaptations in aggressive breast tumors. Metabolomic analysis of MDA-MB-468 cell culture media reveals distinct metabolic footprints that highlight the tumor’s reliance on key nutrients such as glucose and glutamine. The metabolic profiling of TNBC patient serum, however, shows significant differences from MDA-MB-468 culture media, suggesting that in vitro models may not fully replicate systemic metabolic changes in patients. In TNBC patient serum, elevated levels of glucose, glutamine, and citrate contrast with decreased levels of lactate, alanine, and tyrosine, indicating altered energy metabolism and amino acid utilization. MDA-MB-468 cells display a high rate of lactate secretion, a hallmark of the Warburg effect, whereas TNBC patients show reduced serum lactate, possibly due to systemic metabolic adaptations. The study underscores the limitations of monolayer cell cultures in mimicking the metabolic complexity of TNBC in vivo. These findings emphasize the importance of integrating both in vitro and in vivo metabolic analyses to better understand TNBC biology and improve therapeutic targeting strategies.
Basic study design
- Post collection from flasks, MDA-MB-468 cells used for injection must maintain 98-99% cell viability determined by trypan blue exclusion. The cell suspension is adjusted such that each mouse (athymic BALB/C or NOD/SCID, 10-12 w.o.) receive a single injection containing 1 – 2 million cells. The injection volume is 120-150 µL of the Matrigel plus MDA-MB-468 cell suspension.
- Tumors are then measured with digital calipers until an average size of 150-200 mm3 is reached to begin the study. Animals are randomized into treatment cohorts.
- Tumors are continually measured and mouse weights recorded (up to 2-3 times a week). At study completion, animals are euthanized humanely.
- Collected tissues are performed as defined for termination of experiment and are snap frozen, fixed for histology or isolated for gene expression analysis.
- Tumor samples are weighed and imaged (digital option).
Xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of drugs against specific types of cancer. New medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels). Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC-regulated and GLP-compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression. Our animal facilities have the flexibility to use specialized food or water systems for inducible gene expression systems.
Following options are available for the MDA-MB-468 xenograft model:
- MDA-MB-468 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- MDA-MB-468 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- MDA-MB-468 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, injection into the mammary fat pad)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
