HEK-293 xenograft model
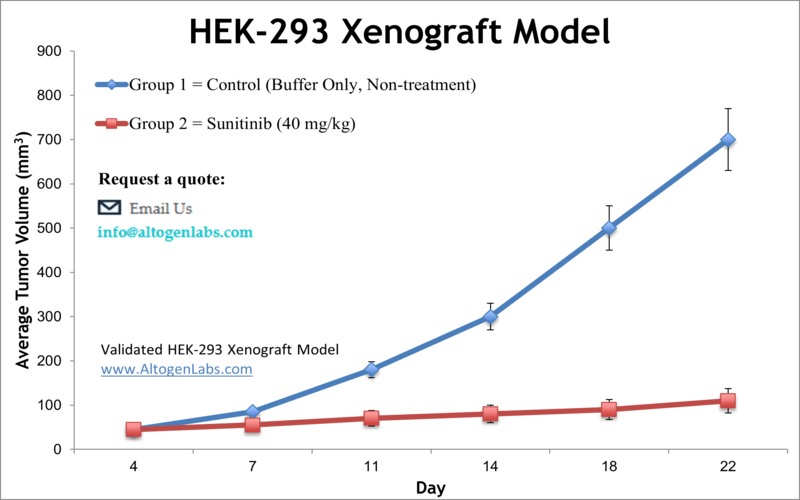
Human embryonic kidney cells have proven to be indispensable tools in cancer research due to their high transfection efficiency and reliable growth. Preclinical xenograft studies utilize cancer cell lines aiming to identify novel anti-cancer agents. The HEK-293 epithelial cell line was isolated from human embryonic kidney cells via the transformation with sheared adenovirus 5 DNA in 1973 in Alex van der Eb’s laboratory in Leiden, the Netherlands. HEK293 is a widely used human embryonic kidney cell line that was originally derived in 1973 from primary cultures of embryonic kidney tissue. The HEK293 cell line has been extensively studied and is widely used in biomedical research as a model system to study various aspects of cell biology, including protein expression, gene regulation, cell signaling, and drug discovery. HEK-293 is a potent tool for producing therapeutic proteins and viruses for gene therapy. A 2005 study in Molecular Cancer Therapeutics investigated the contribution of fibroblast activation protein enzymatic activity to tumor growth in vivo using the HEK293 xenograft mouse model. The study demonstrates that the enzymatic activity of fibroblast activation protein is required for fibroblast activation protein-driven tumor growth. Also, the enzymatic activity of fibroblast activation protein plays a vital role in the promotion of tumor growth, making it useful for therapeutics altering fibroblast activation protein-induced tumor growth. Another study to use the Hek-293 model is by Voce et al. (2011) which demonstrated in xenograft tumors that the multikinase inhibitor sunitinib, which is known for its anti-angiogenic and subsequent antitumor effects, inhibits tumor vasculature growth through an Akt- and ERK-phosphorylation independent manner. This is important when considering potential combination therapies for overcoming resistance. The study by Cheng et al. (2002) also used the HEK-293 mouse xenograft model to show that fibroblast activation protein (FAP), a type 2 integral membrane glycoprotein in the serine protease family, promotes tumor growth and supports its potential as a therapeutic target. A 2010 study (Debeb et al.) characterized HEK-293 cells and found that they exhibit carcinogenic stem cell-like phenotype in 3D spheres in that they are resistant to radiation, upregulate beta-catenin, Notch1, surviving, mesenchymal genes, pro-metastatic genes and miRNAs involved in metastasis and self renewal. These data support the use of these cells as a cancer stem cell model. The HEK-293 cell line (human kidney) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) HEK-293 xenograft mouse model. The HEK-293 xenograft model is currently utilized in preclinical research addressing the anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor efficacy of kinase inhibitors (e.g. sunitinib) or increasing CDC273 expression levels by introduction of an antagomir (e.g. miR-155) to increase apoptosis.
Download Altogen Labs HEK-293 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design:
- HEK-293 cells are trypsinized, and viable cell numbers are determined. Trypan blue exclusion is used to ensure highly viable cells are inoculated. The injection contains 1 x 106 cells in a volume of 100 µL (Matrigel plus HEK-293 cells).
- Athymic BALB/C or NOD/SCID mice (9-10 weeks old) receive injections in the hind leg (subcutaneously). Manual palpation of inoculation areas determine tumor establishment. At 50-150 mm3in size, animals are randomized into study groups. Test compound dosing follows the treatment schedule.
- Tumors (daily measurements) and body weights (bi-weekly) are documented. Tumor sizes of 2,000 mm3 (or the study tumor size limit per IACUC) signals the end of the study.
- Necropsies enable collection of tissues studied in downstream analysis. Resected tumors are excised/weighed/documented via digital imaging. Tissues are stored according to parameters defined by the customer: frozen, stabilized in RNAlater, prepared for histology, or nucleic acids isolated.
Get Instant Quote for
HEK-293 Xenograft Model
Researchers investigating the role of specific proteins or gene products in regulating tumor growth can benefit from development of protein overexpression (genetically engineered to ectopically express proteins, tumor suppressors, or oncogenes) and RNAi cell lines with long term gene silencing. Altogen Labs provides quantitative gene expression analysis of mRNA expression (RT-PCR) and protein expression analysis using the WES system (ProteinSimple). The dosing of the experimental compound of interest is initiated, for a staged study, when the mean tumor size reaches a specified volume (typically 50-100 mm3). In an unstaged study, the dosing of the compound of interest is initiated 4-5 days after xenotransplantation. Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC regulated and GLP compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression.
Following options are available for the HEK-293 xenograft model:
- HEK-293 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- HEK-293 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- HEK-293 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 25-30 mg/kg
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
