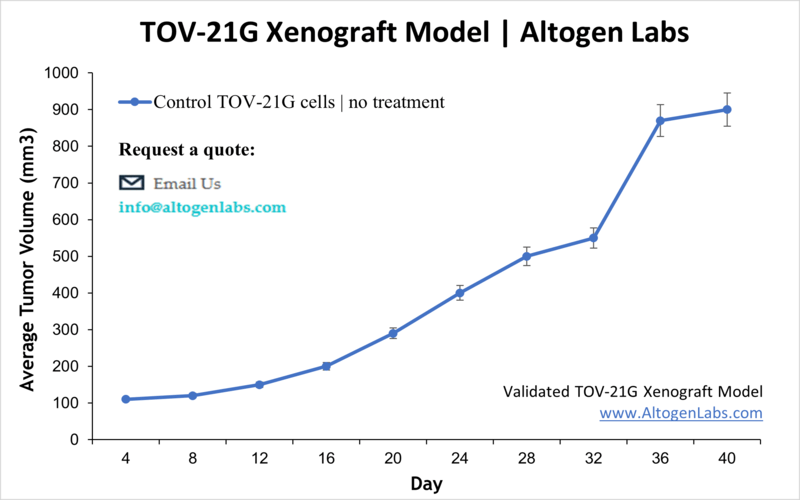
TOV-21G Xenograft Model
The age group at highest risk for ovarian cancer is women over 40. Ovarian cancers may affect different cells types within the ovaries: germ cell tumors (start in the ova aka egg-producing cells), epithelial tumors ( affect the ovary surface covering), or stromal tumors (hormone-producing structural cells). TOV-21G cells were derived in 1991 from a 62 year old patient with no ovarian cancer family history. Many studies have used the TOV-21G. Miura et al. published an International Journal of Oncology article (2015) investigating the effects of carbonyl reductase 1 (CR1) using the TOV21G model. Results demonstrated that overexpression of CR1 leads to decreased tumor volume and increased expressions of caspases and tumor necrotic factor receptor 1 leading to increases in apoptosis. Kashiyama et al. (PLOS ONE, 2014) used TOV-21G cells to characterize DS-7423, a novel PI3K and mTOR dual inhibitor, in ovarian cancer. Data suggested that treatment with DS-7423 exhibits antitumor effects including TP53-dependent apoptosis induction in ovarian clear cell adenocarcinoma (OCCA). Finally, a Clinical Cancer Research article (Beltran et al., 2014) studied ganitumab (AMG 479), an insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-IR), in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy (e.g. cisplatin, paclitaxel, carboplatin). Data showed that while ganitumab inhibited IGF-IR expression and tumor growth, this effect was synergistic with in combination with platinum based therapies. Additionally, results demonstrated that PTEN mutations resulted in ganitumab resistance, which has clinical implications for screening those who would most benefit from this treatment. The TOV-21G cell line is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) TOV-21G xenograft mouse model. The TOV-21G xenograft model has been used to investigate ovarian oncology pathways, dual tyrosine kinase inhibitors, cisplatin, IGF-IR inhibitors, etc.).
Basic Study Design
- TOV-21G cells are maintained in exponential growth phase under aseptic conditions.
- Cells are trypsinized and cell count viability is determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay (98% of cell viability is required). TOV-21G cell suspension is adjusted to appropriate density.
- Each mouse is singly subcutaneously injected into the right flank with 106 cells in 100-200 µL of a Matrigel-TOV21G cells suspension.
- The injection sites are palpated up to three times weekly until tumors are established to an average size of 50-100 mm3 as measured by digital calipers.
- Animals are randomized into treatment groups. Administration of test compound is performed according to the pre-established treatment schedule.
- Mice weights are measured and recorded 3 times weekly; tumors are measured and recorded daily.
- End of study is reached when tumor size reaches 2,000 mm3 or the predetermined size limit per approved IACUC protocol.
- Final necropsy and tissue collections are performed for appropriate downstream analysis. Tumors are excised, weighed and documented by digital imaging. Tumors and tissues can be stabilized in RNAlater, snap frozen in LN2 or prepared for histology.
