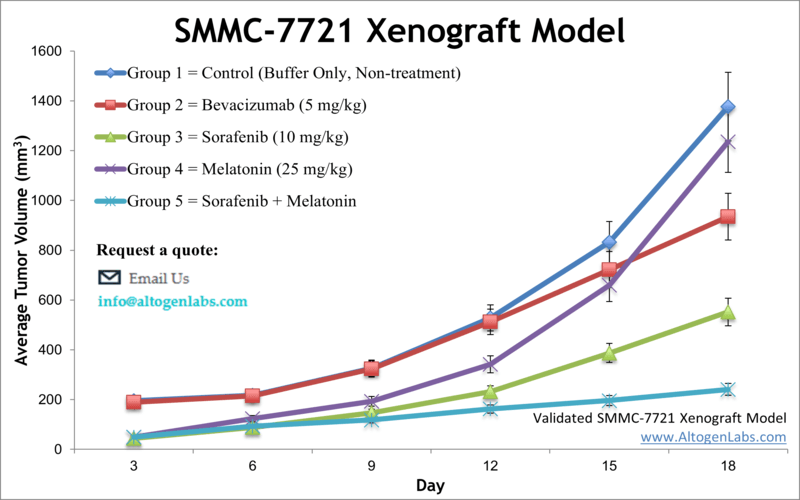
SMMC-7721 xenograft model
SMMC-7721 is a human hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cell line that was established from a liver tumor of a Chinese patient. HCC is the most common type of liver cancer, and the SMMC-7721 cell line is commonly used as a model to study the molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies for this disease. Hepatocellular carcinoma is one of most prevalent malignancies worldwide and originates in hepatocellular cells, accounting for nearly 70 percent of all liver cancers. Xenograft animal models are highly utilized to assess the efficacy of novel drugs, providing the opportunity to screen new therapeutic approaches. The SMMC-7721 cell line was derived from an Asian male patient with hepatocellular carcinoma in 1977. Human hepatoma cell line SMMC-7721 expresses EGFR and VEGFR and is an invaluable tool in liver cancer research. A 2012 study published in APJCP (Asian Pacific Journal of Cancer Prevention), evaluates antiproliferative activity and underlying mechanisms of Tas13D, a novel taspine derivative in vivo, using the SMMC-7721 xenograft model. The article demonstrates that 13D inhibits SMMC-7721 xenograft tumor growth and reduces SMMC-7721 cell proliferation, which could be beneficial for liver cancer patients. A 2014 Cancer Cell study (Yuan et al.) identified a long noncoding RNA, lncRNA-ATB, which is activated by TFG-beta in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC); they also observed that downstream effects include epithelial to mesenchymal transition, invasion, activating the STAT3 cascade and promoting an autocrine-induced activation of IL-11. This study supports lmcRNA-ATB as a potential antimetastatic drug target. A 2017 study (Gao et al.) characterized the effect of borrelidin, a compound produced by actinomycete bacteria which has anti-viral, anti-bacterial, anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activity, in HCC. Using the SMMC-7721 cell model results from this study revealed a MAPK-mediated suppression of tumor growth and cell cycle arrest. The last example study is by Wu et al. (2018) in which the traditional Chinese medicine Dahuang zhechong pill (DHZCP) was shown to overcome doxorubicin resistance in HCC via upregulation of pro-apoptitic proteins and a negative impact on energy metabolism. The SMMC-7721 cell line (human liver) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) SMMC-7721 xenograft mouse model. The SMMC-7721 xenograft model is a preclinical setting for clients to study novel, low toxicity antitumor therapeutics (e.g. LfcinB-P13, 6-Shogaol) or combinatorial therapies that incorporate the standard of care therapeutic, sorafenib (e.g. CH12: monoclonal antibody against EGFRvIII).
Download Altogen Labs SMMC7721 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- All cell flasks are maintained at exponential growth prior to collection.
- After trypsinization, cell count and cell viability is examined by trypan blue exclusion. Density of the cells are adjusted such that 1 x 106 cells are inoculated in a 0.1-0.2 mL inoculation (Matrigel + SMMC-7721 cells). Subcutaneously, injections are made into the hind leg of athymic nu/nu or NOD/SCID mice (10-11 weeks old).
- Randomization into treatment cohorts marks the start of the in-life portion of the study. All test compounds are administered according to client supplied concentrations and dose schedules.
- All tumor measurements are recorded (up to daily measurements), including mouse body weight measurements (bi-weekly).
- Study conclusion is reached at the tumor size limit per approved IACUC protocol (usually 2,000 mm3), and necropsies are performed. Client instructions determine which tissues are collected and method of storage (frozen, 10% NBF, RNAlater, etc). Tumors are dissected, then weighed; optional digital imaging is available upon request.
Get Instant Quote for
SMMC-7721 Xenograft Model
Xenograft animal models are used to assess the effectiveness of drugs against specific types of cancer. New medicines are tested on staged tumor growths that have been engrafted via subcutaneous or orthotopic inoculation in an immunocompromised mouse or rat model. All clinically approved anti-cancer agents have been evaluated with conventional preclinical in vivo models. Xenograft studies can be highly complex, starting with the selection of the appropriate animal model, choice of tumorigenic cell line, administration method, dosing, analysis of tumor growth rates and tumor analysis (histology, mRNA and protein expression levels).
Altogen Labs provides an array of laboratory services using over 100 standard CDX models and 30+ PDX xenograft models. Researchers investigating the role of specific proteins or gene products in regulating tumor growth can benefit from development of protein overexpression (genetically engineered to ectopically express proteins, tumor suppressors, or oncogenes) and RNAi cell lines with long term gene silencing. Altogen Labs provides quantitative gene expression analysis of mRNA expression (RT-PCR) and protein expression analysis using the automated WES system.
The dosing of the experimental compound of interest is initiated, for a staged study, when the mean tumor size reaches a specified volume (typically 75-150 mm3). In an unstaged study, the dosing of the compound of interest is initiated immediately after xenografting. Mice are dosed once or twice a day for 28 days (or other desired study duration) via the chosen route of administration. Tumor volume (mm3) is calculated via the “(W x W x L) / 2” formula, where W is tumor width and L is tumor length.
Following options are available for the SMMC-7721 xenograft model:
- SMMC-7721 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- SMMC-7721 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- SMMC-7721 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide, at a dosage of 10-20 mg/kg administered by intramuscular injection to the control group daily for the study duration
