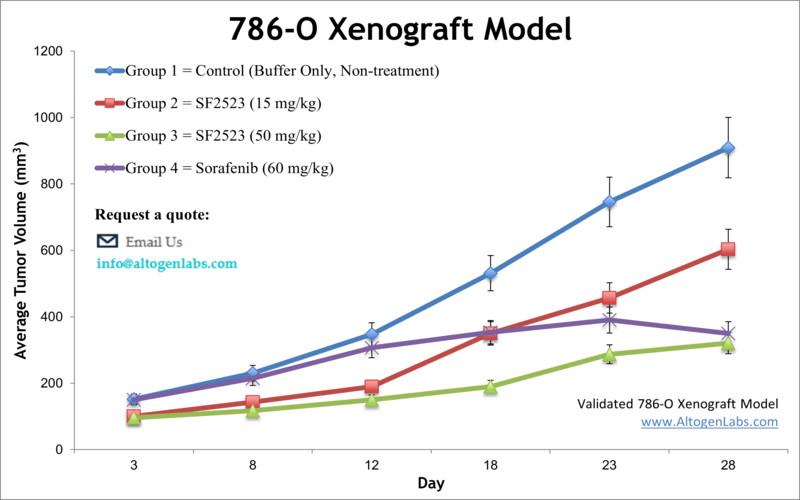
786-O Xenograft Model
The most common type of kidney cancer is renal cell carcinoma (RCC), accounting for nearly 3 percent of tumors in adults. The exact cause of renal cell carcinoma is currently unknown. Xenograft rodent models are essential in preclinical studies for testing novel therapeutic modalities to address renal cancer. The 786-O epithelial cell line is isolated from primary adenocarcinoma cells of the kidney tissue of a 58-year-old Caucasian male patient with renal cell adenocarcinoma. 786-O is a hypertriploid cell line that produces parathyroid hormone (PTH) and is tumorigenic in nude mice. 786-O is one of the first RCC cell lines that is commonly used in RCC-focused research. A 2013 renal xenograft study published in British Journal of Cancer, demonstrates that resistance to sunitinib is accompanied by increased COX-2 expression in areas of tumor hypoxia in the 786-O xenograft model. Also, the COX-2 inhibitor celecoxib enhances the effectiveness of sunitinib in the 786-O xenograft model by delaying time to progression if administered early in the course of sunitinib therapy. Celecoxib showed activity in the 786-O tumor model as a single agent and in combination with sunitinib. The 786-O RCC line expresses high levels of VEGF (Vascular endothelial growth factor), which stimulates angiogenesis and gives rise to tumors in nude mice. A 2010 study (Bhatt et al.) used the 786-O model to study the mechanism of resistance that often surfaces within 6-12 months of anti-angiogenesis treatment of metastatic renal cancer. Their results demonstrated that treatment with either sunitinib or sorafenib initially targeted VEGF however resistance was in part due to resumption of angiogenesis correlated to downregulation of IFN-gamma angiostatic chemokines; when the conventional chemotherapies were combined with CXCL9 (one of the angiostatic chemokines) treatment, prolonged reduction of angiogenesis was observed thus providing potential combination clinical strategies for overcoming resistance. Lastly, a 2017 Tumor Biology study used the 786-O model to demonstrate that Rap2B can promote angiogenesis through PI3K/AKT pathway in vivo, and loss of Rap2B could be a novel strategy for RCC anti-angiogenesis therapy. The 786-O cell line (human kidney) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) 786-O xenograft mouse model that allows researchers to study COX-2 inhibitors and anti-angiogenesis therapy as well as anti-cancer agents targeting RCC cells.
786O Xenograft Model. Download PDF: ![]()
Download Altogen Labs 786O Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Subcutaneous 786-O Xenografts in Renal Cancer Research
Renal cell carcinoma (RCC), particularly its clear cell subtype, presents a major clinical challenge due to its genetic heterogeneity, high metastatic potential, and resistance to conventional treatments. Although targeted therapies and immunotherapies have improved outcomes, many patients develop resistance or relapse. To address this, xenograft models derived from RCC cell lines or patient tumors are widely used to study tumor growth, angiogenesis, and drug response in vivo. These models are essential for bridging the gap between in vitro research and clinical application, though limitations such as the absence of immune components and tumor heterogeneity remain. Subcutaneous xenograft transplantation using the 786-O renal cell carcinoma cell line remains a widely utilized preclinical model for studying the tumorigenic behavior and therapeutic responsiveness of clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC). The 786-O cell line, characterized by inactivation of the von Hippel–Lindau (VHL) tumor suppressor and consequent constitutive expression of hypoxia-inducible factor 2-alpha (HIF-2α), recapitulates key molecular features of advanced ccRCC, including angiogenic signaling and metabolic reprogramming. In this model, 786-O cells are typically injected subcutaneously into immunodeficient mice, such as athymic nude or NOD/SCID strains, leading to reproducible tumor formation that facilitates longitudinal measurement of tumor volume and assessment of therapeutic efficacy. Subcutaneous implantation offers technical simplicity, robust tumor engraftment rates, and accessibility for tumor monitoring, making it an effective platform for evaluating targeted therapies, including HIF-2α inhibitors and anti-angiogenic agents. The model has been instrumental in elucidating mechanisms of drug action and resistance and has supported the preclinical validation of agents now in clinical use. However, a notable limitation is the absence of an intact immune microenvironment, which precludes evaluation of immune-based therapies and limits the model’s applicability to immuno-oncology. Additionally, the subcutaneous site does not fully recapitulate the orthotopic tumor microenvironment of the kidney. Despite these constraints, the 786-O subcutaneous xenograft model remains a critical tool in translational kidney cancer research, providing a biologically relevant and experimentally tractable system for preclinical drug development and mechanistic studies.
ER Stress and AKT Inhibition Drive Apoptosis in 786-O Cells
Norcantharidin (NCTD) exhibits potent cytotoxicity in the 786-O renal carcinoma cell line through mechanisms involving mitochondrial dysfunction, endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and inhibition of the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. NCTD selectively reduced 786-O cell viability in a dose- and time-dependent manner while sparing normal renal epithelial cells, suggesting therapeutic selectivity. Apoptotic induction was confirmed by sub-G1 cell cycle arrest, Annexin V positivity, and cleavage of caspases and PARP, indicating engagement of both intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways. Mitochondrial depolarization, upregulation of Bax, and downregulation of Bcl-2 and Mcl-1 further implicated mitochondrial signaling in cell death. Concurrently, NCTD triggered robust ER stress, marked by elevated levels of Grp78, CHOP, ATF4, and phosphorylated eIF2α, while pharmacologic inhibition of ER stress via salubrinal partially reversed apoptotic outcomes. Additionally, NCTD suppressed phosphorylated AKT, and constitutive AKT overexpression mitigated apoptosis and restored anti-apoptotic protein expression, suggesting that AKT inactivation acts downstream of ER stress and amplifies cell death signaling.
Immuno-oncology Xenograft Models
Altogen Labs is a preclinical contract research organization specializing in the investigation and translational development of novel pharmacological and biologic therapeutics, with a focus on oncology, immunotherapy, vaccine platforms, dermatological agents, and bioactive natural products. The facility is staffed by experienced scientific personnel and equipped with advanced instrumentation to support high-throughput in vivo and in vitro studies. A key area of expertise includes immuno-oncology, with established capabilities utilizing both humanized and immunodeficient murine models engrafted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs), CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells, and induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to evaluate immune reconstitution, therapeutic efficacy, and safety parameters. Central to Altogen Labs’ platform is a curated library of more than 100 internally validated xenograft models, including cell line-derived xenografts (CDX), patient-derived xenografts (PDX), patient-derived cell cultures (PDC), and patient-derived organoids (PDOrg), offering clinically relevant systems for predictive drug response and biomarker discovery. These models support comprehensive efficacy testing for small molecules, biologics, and combination therapies. The laboratory also provides GLP-compliant toxicology services encompassing acute, sub-chronic, and chronic exposure studies to characterize dose-dependent toxicity, identify target organ effects, and determine the therapeutic index of investigational compounds. This integrated approach enables efficient progression from early-stage discovery to IND-enabling studies across a wide range of therapeutic modalities.
Apoptotic Regulation and Therapeutic Vulnerabilities in 786-O Renal Carcinoma
Characterized by loss of functional VHL protein, the 786-O renal carcinoma cell line displays constitutive activation of hypoxia-inducible factors and downstream pro-survival signaling cascades. This molecular phenotype contributes to its resistance to apoptosis and enhanced tumorigenicity. One of the defining therapeutic response patterns in 786-O cells is their sensitivity to norcantharidin-induced apoptosis, which occurs through coordinated disruption of mitochondrial integrity, activation of endoplasmic reticulum stress pathways, and suppression of AKT-mediated survival signaling. Apoptotic markers such as caspase cleavage, mitochondrial membrane depolarization, and modulation of Bcl-2 family proteins are consistently observed, along with increased expression of ER stress-related proteins including CHOP and phosphorylated eIF2α. Furthermore, inhibition of ER stress or forced activation of AKT attenuates the cytotoxic response, indicating a tightly regulated, multi-axis control of apoptosis in this cell line. These mechanistic insights reveal a vulnerability in VHL-deficient renal cancer cells that can be therapeutically exploited through agents that simultaneously target metabolic stress responses and oncogenic survival pathways. Serving as a reproducible and genetically defined model, the 786-O cell line has become a cornerstone in the study of apoptosis regulation in renal carcinoma, particularly within the context of hypoxia-adapted tumors. Its use in both in vitro and in vivo systems has yielded reliable results across multiple apoptotic assays, including cell viability, flow cytometry, protein immunoblotting, and xenograft tumor regression. However, its lack of metastatic potential and relatively homogeneous genetic background limit its utility in modeling tumor heterogeneity or resistance evolution. These limitations underscore the importance of integrating orthotopic and patient-derived models to validate therapeutic mechanisms. Despite its origin in renal cancer, the apoptotic vulnerabilities uncovered in 786-O cells, particularly the interplay between ER stress and AKT signaling, have broader relevance for other tumor types. Gastric cancers that exhibit aberrant PI3K/AKT activation or dependence on stress-response pathways may similarly respond to dual-targeting strategies that disrupt both metabolic and survival signaling. Future investigations should examine the applicability of these findings in gastric tumor models, assess synergy with immunomodulatory agents, and further define molecular predictors of treatment response.
786O Xenograft Model. Download PDF: ![]()
Basic study design
1. 786-O cells are cultured under aseptic conditions in exponential growth phase prior to injection.
2. The cells are trypsinized from the flasks and viable cell counts are determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay (98% cell viability required). The cell suspension is adjusted to the appropriate density.
3. Each mouse (athymic BALB/C or NOD/SCID, 10-12 w.o.) receive a subcutaneous injection in the flank of the hind leg of one million cells in a volume of 100 microliters of Matrigel 786-O cell suspension.
4. The injection sites are manually palpated three times weekly until tumors are established. Tumors are measured using digital calipers until they reach an average size of 50-150 mm3.
5. Animals are randomized into treatment cohorts and administration of the compound of interest is performed according to the treatment schedule.
6. Tumors are measured daily and mouse weights recorded 3 times weekly.
7. Animals are euthanized when tumor size reaches 2,000 sq. millimeters or the IACUC protocol predetermined size limit.
8. Necropsy and tissue collections are performed as defined for termination of experiment.
9. Tumors are excised, weighed and documented by digital imaging.
10. Standard gross necropsies are performed and tissues are collected for downstream analysis.
11. Tumors and tissues are snap frozen in LN2 and prepared for histology or gene expression analysis.
Get Instant Quote for
786-O Xenograft Model
Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is IACUC-regulated and GLP-compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression.
Following options are available for the 786-O xenograft model:
- 786-O Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- 786-O Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- 786-O tumor immunohistochemistry
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies
