MIA PaCa-2 xenograft model (subcutaneous and metastatic)
Advanced stages of pancreatic cancer are often fatal and approximately 5 percent of those affected will be alive 5 years after the diagnosis, per the National Pancreatic Cancer Foundation. The MIA PaCa-2 epithelial cell line was initially isolated in 1975 using pancreatic tumor cells of a 65-year-old Caucasian male patient with pancreatic adenocarcinoma. MIA PaCa-2 is a hypotriploid cell line that has a doubling time of nearly 40 hours. A 2017 study by Shiomi et al. published in Anticancer Research, investigated the anti-tumor mechanism of Z-360, a gastrin/cholecystokinin-2 receptor (CCK2R) antagonist, in MIA PaCa-2 cells and the MIA PaCa-2 subcutaneous xenograft model. These findings indicate that Z-360 significantly decreases the tumor weight and suppresses the expression of anti-apoptosis factors such as survivin, XIAP and Mcl-1. Moreover, the combination treatment of Z-360 and gemcitabine was shown to be more effective. A 2012 Anticancer Research article by Yoon et al. used the MIA PaCa-2 cell line to evaluate YM155, a suppressor of the anti-apoptotic regulator survivin, in combination with gemcitabine. Results demonstrated that gemcitabine treatment resulted in an up-regulation of survivin and that combination therapy with YM155 resulted in enhanced chemosensitivity. In 2011 Nature published a study (Andrieu et al.) which used the Mia PaCa-2 model to investigate OGX-427, an Hsp27 inhibitor which had been used in other Phase II clinical trials for ovarian, breast, prostate and bladder cancer types. Results showed that OGX-427 treatment in cell and xenograft Mia Paca-2 models resulted in apoptosis induction as well as enhanced gemcitabine sensitivity, thereby providing a clinically relevant potential strategy for pancreatic cancer treatment. Finally, Schultz et al. released an Oncology Research study (1993) that used the Mia PaCa-2 xenograft model to evaluate then-novel anticancer agents including diarylsulfonylureas (DSU), taxol, Adriamycin, cisplatin, 5-fluorouracil and taxol, many of which are now well-known chemotherapy agents. The MIA PaCa-2 cell line (human pancreas) is used to create the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) MIA PaCa-2 xenograft mouse model. The MIA PaCa-2 xenograft model exhibits tumor growth inhibition and chemosensitization utilizing monotherapies or in combination (e.g. sulindac, LC-1, parthenolide, gemcitabine).
Download Altogen Labs MiaPaCa2 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- Each mouse (athymic BALB/C or NOD/SCID, 10-12 w.o.) will receive a single injection (s.c.) into a hind leg. The injection contains one million cells (100-200 µL vol) of the Matrigel plus MIA PaCa-2 suspension.
- The injection sites are monitored until tumors are established. Tumors are then calipered until they reach 100-150 mm3. At this point, animals are randomized into necessary treatment cohorts. The test compounds are administered according to treatment schedule.
- Daily tumor measurements are logged. Mouse weights are recorded 3 times weekly.
- During the end of study necropsy, a list of customer defined tissues are collected.
- Tumors are excised from the animals during necropsy, then weighed and documented (digital imaging).
Metastatic Model
CDX models are mouse xenografts used in pre-clinical therapeutic studies. However, as primary tumors proliferate they invade surrounding tissue, become circulatory, survive in circulation, implant in foreign parenchyma and proliferate in the distant tissue. This result leads to an extremely high percentage of death in cancer patients due to metastasis. Metastatic tumor mouse models are utilized to develop novel therapeutic agents that target metastasis (anti-metastatic therapeutics).
To create a metastatic model, the cell line of interest is transfected with vectors containing green fluorescent protein (GFP) or luciferase. Maintained under antibiotic selection, only cells containing the integrated vector will survive. The new cell line clones are capable of stably expressing the gene of interest and are used in metastatic mouse model studies. Although each new cell line clone may contain its own inherent difficulties, the new cell line contains the ability to track internal tumor progression via bioluminescence (luciferase fluorescence after injecting luciferin) or fluorescence (GFP). Internal orthotopic and metastatic tumor growth (not palpable) can now be measured throughout the study, enabling a researcher to gain more insight and additional data in contrast to relying on end of study tumor weight measurements.
Case Study: U87-luc Xenograft Model
An example of Altogen Labs utilizing a luciferase expressing cell line to monitor orthotopic tumor growth is exhibited below. The same ideology of tumor observation is incorporated in metastatic tumor models.
Luciferase expressing U87-luc cells were implanted and tumors allowed to grow. Tumor growth was monitored in a Night Owl (Berthold Technologies) imaging system 10 minutes after an intraperitoneal (IP) injection of the luciferin substrate. As seen in the example below, luciferase expression (measured as photons emitted) in the U87-luc model grants the researcher a visual image and quantifiable metric for orthotopic or metastatic tumor progression.
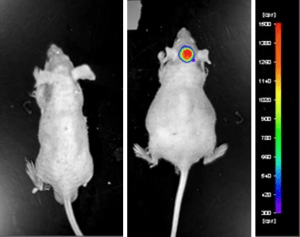
Figure 1. Luciferase expression in U87-luc orthotopic model. Control and implanted glioma mouse model fluorescence was analyzed 10 minutes after intraperitoneal luciferin injection.
View full details of the case study by clicking here.
Get Instant Quote for
MIAPaCa-2 Xenograft Model
Altogen Labs provides an array of laboratory services using over 90 in-house validated CDX models and over 30 PDX models. The dosing of the experimental compound of interest is initiated, for a staged study, when the mean tumor size reaches a specified volume (typically 100-150 mm3). In an unstaged study, the dosing of the compound of interest is initiated immediately after xenotransplantation. Mice are dosed once or twice a day for 28 days (or other desired study duration) via the chosen route of administration. Tumor volume (mm3) is calculated via the “(W x W x L) / 2” formula, where W is tumor width and L is tumor length. Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facility is GLP-compliant and regulated by IACUC. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis).
Following options are available for the MIA PaCa-2 xenograft model:
- MIA PaCa-2 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- MIA PaCa-2 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- Dosing route (intravenous, intratracheal, continuous infusion, intraperitoneal, intratumoral, oral gavage, topical, intramuscular, subcutaneous, intranasal, using cutting-edge micro-injection techniques and pump-controlled IV injection)
- MIAPaCa-2 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing dox or cyclophosphamide
