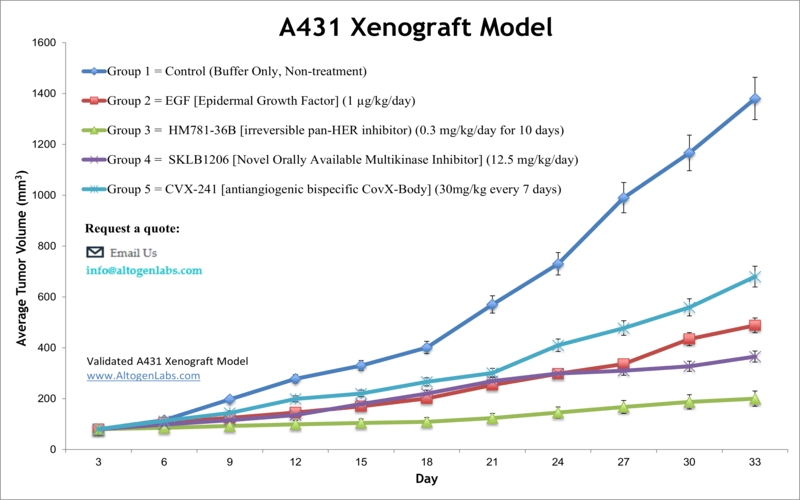
A431 xenograft model
The A431 cell line is a human epidermoid carcinoma cell line that was derived from a skin tumor of a patient in 1978. A431 cells are commonly used in cancer research to study the biology of skin cancer and test new therapies. Squamous cell carcinoma or epidermoid carcinoma is one of the most prevalent types of skin cancer. It develops from squamous cells and can be triggered by UV exposure. The A431 cell line was isolated from epidermal cells of an 85-year-old female with epidermoid carcinoma. A431 is commonly used for studies of skin cancer as well as for pharmaceutical and biomedical purposes. Targeting agents of the EGFR-related signaling pathway show promising anticancer activities in skin cancer patients. Furthermore, preclinical studies of the combined use of radiotherapy (RT) and EGFR inhibitors indicate that the inhibition of EGFR increases the therapeutic efficacy of fractionated irradiation. In 1992 Robinson et al. (International Journal of Oncology) characterized the A431 xenograft model as an appropriate model for testing EGFR antagonists by demonstrating inhibition of tumor growth as a response to EGFR targeted treatments. A 2015 article by Lim et al. published in Cancer Research and Treatment evaluated the tumor growth suppression and radiation-sensitizing effects of an exogenous epidermal growth factor (EGF) in the A431 xenograft model in vivo. These findings demonstrate the anti-tumor effect of EGF in vivo and show the potential role of EGF as a radiation sensitizer. Gong et al. published a Neoplasia article (2010) using the A431 xenograft model to study the binding of their developed EGFR Affibody molecule (Eaff) that has a conjugated near infrared dye (NIR dye) IRDye800CW maleimide. Results showed that the Eaff molecule was able to show inhibition without activating EGFR signaling pathways, which could provide a method for clinical imaging of EGFR-overexpressing tumor cells. Finally, a 2009 Cancer Gene Therapy article by Ho et al. used the A431 xenograft model to test the anticancer properties of an EGFR-targeted monoclonal antibody using gene-based delivery, which is a technique that addresses the limiting production and purification processes of antibody based therapy. Results from the study demonstrate sustained and high in vivo expression of the EGFR antibody after delivery via adeno-associated virus (AAV) 2/1. The expression of the EGFR Ab successfully and significantly inhibited tumor growth which has clinical implications for more widely available gene-based delivery of antibody therapy. The A431 cell line (human squamous carcinoma) is used for creating the CDX (Cell Line Derived Xenograft) A431 xenograft mouse model. This CDX model is a proven model that is sensitive to EGF inhibitor therapeutics.
Download Altogen Labs A431 Xenograft Model PowerPoint Presentation: ![]()
Basic study design
- Cells are maintained at the exponential growth phase prior to injection.
- A431 cells are collected by trypsinization and prepared for injection. Viable cell counts are then determined using a trypan blue exclusion assay (98% cell viability required). The cell suspension is then adjusted to the appropriate density.
- Each of the mice (athymic BALB/c nude) will receive a subcutaneous injection (s.c) in the flank of a hind leg containing one million cells. The volume of the injection is 100 µL of the Matrigel A431 cell suspension.
- Three times weekly, the injection sites are palpated until it is determined that tumors are established. Tumors are measured with digital calipers until they reach the required starting volume.
- Animals are randomized into cohorts and the administration of the test compound is performed following the treatment schedule.
- Tumors are measured daily, with mouse weights recorded 3 times weekly.
- Animals are euthanized as tumor size reaches 2,000 mm3 or at IACUC-determined size limit.
- The necropsy is performed as defined for termination of experiment.
- Tumors are excised and weighed. Tumors are documented by digital imaging.
- Standard necropsies are performed to collect tissues for downstream analysis.
- All tissues can be stabilized in RNAlater reagent, snap frozen in LN2or prepared for gene expression analysis.
Get Instant Quote for
A431 Xenograft Model
Altogen Labs provides an array of laboratory services using over 90 standard cell line derived xenograft (CDX) models and over 30 PDX models. Researchers investigating the role of specific proteins or gene products in regulating tumor growth can benefit from development of protein overexpression (genetically engineered to ectopically express proteins, tumor suppressors, or oncogenes) and RNAi cell lines with long term gene silencing. Altogen Labs provides quantitative gene expression analysis of mRNA expression (RT-PCR) and protein expression analysis using the automated western blot WES system.
Animal handling and maintenance at the Altogen Labs facilities are IACUC regulated and GLP compliant. Following acclimation to the vivarium environment, mice are sorted according to body mass. The animals are examined daily for tumor appearance and clinical signs. We provide detailed experimental procedures, health reports and data (all-inclusive report is provided to the client that includes methods, results, discussion and raw data along with statistical analysis). Additional services available include collection of tissue, histology, isolation of total protein or RNA and analysis of gene expression. Our animal facilities have the flexibility to use specialized food or water systems for inducible gene expression systems.
Following options are available for the A431 xenograft model:
- A431 Tumor Growth Delay (TGD; latency)
- A431 Tumor Growth Inhibition (TGI)
- Dosing frequency and duration of dose administration
- A431 tumor immunohistochemistry
- Alternative cell engraftment sites (orthotopic transplantation, tail vein injection and left ventricular injection for metastasis studies, injection into the mammary fat pad, intraperitoneal injection)
- Blood chemistry analysis
- Toxicity and survival (optional: performing a broad health observation program)
- Gross necropsies and histopathology
- Positive control group employing cyclophosphamide or dox
- Lipid distribution and metabolic assays
- Imaging studies: Fluorescence-based whole body imaging
